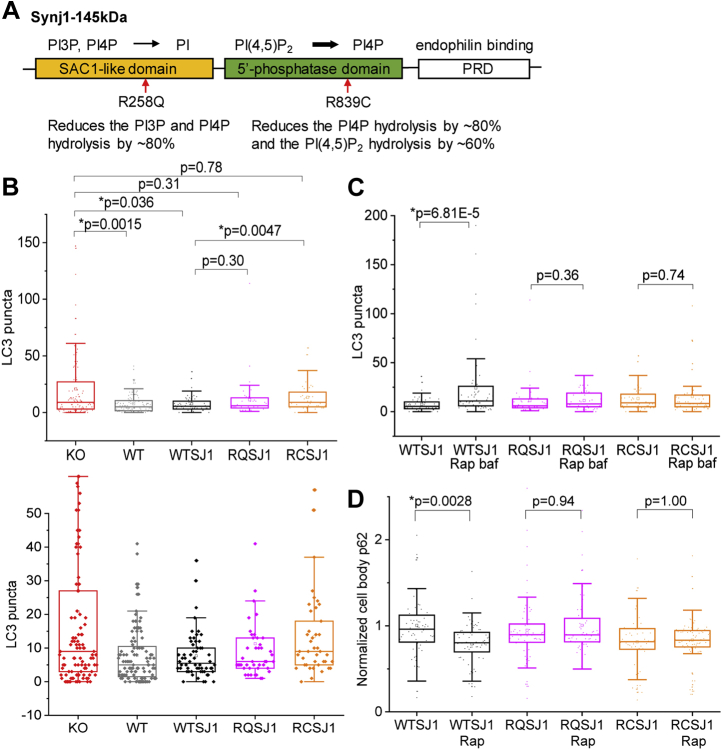
Figure 5.
The Synj1 phosphatase domains play a major role in regulating astrocyte autophagosome formation.A, domain structure and function of Synj1 with arrows pointing to the known Parkinsonism mutations illustrated by the functional outcome of the mutations reported in our previous publication (25). B–D, WT hSynj1 (WTSJ1), R258Q hSynj1 (RQSJ1), or R839C hSynj1 (RCSJ1) were expressed in the Synj1 KO astrocytes and compared with the KO and its littermate WT astrocyte culture. B, box plots comparing the number of LC3 puncta at the basal level with 1-h baf treatment for all groups. C and D, box plots comparing the rapamycin-induced autophagy markers, the number of GFP-LC puncta (C) and p62 (D) in KO cells expressing WT hSynj1 (WTSJ1), R258Q hSynj1 (RQSJ1), or R839C hSynj1 (RCSJ1). p Values for the LC3 analyses are from Mann–Whitney U tests. p Values for p62 analyses are from Tukey's post hoc tests following two-way ANOVA. Synj1, Synaptojanin1.