Fig. 1.
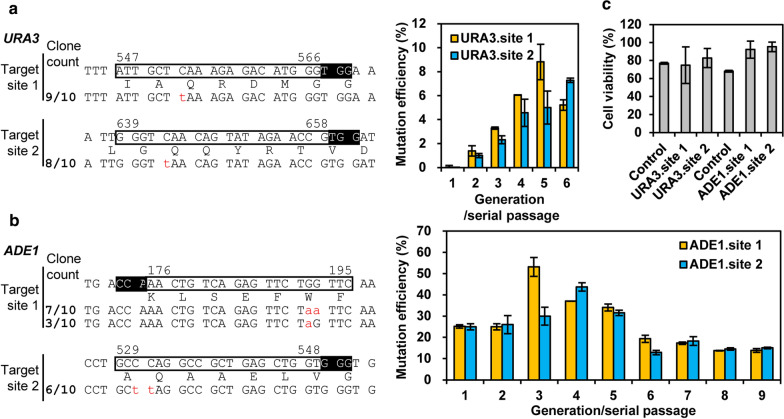
Base editing mediated genomic mutagenesis. a Two target sites in URA3 gene were selected for editing by Target-AID based on the criteria that the cytosine mutations in the − 20 to − 13 position may introduce a stop codon, resulting in a 5-FOA resistance phenotype. b Two target sites in ADE1 gene were selected for introducing a stop codon by Target-AID, resulting in a red colony phenotype. In a and b, sequences of identified mutations are aligned with the number of colonies over the number of total sequenced colonies for each phenotype change (5-FOA resistance or red colony color). Mutation frequencies of several serial passages are charted on the right. Reference wild-type sequences with translated amino acid sequences are shown with the PAM sequence (inverted) and the target site (box). The target sequence of ADE1 site 1 is complementary to the sequence shown. c Effect of base editing on cell viability. Error bars represent standard deviation among biological triplicates