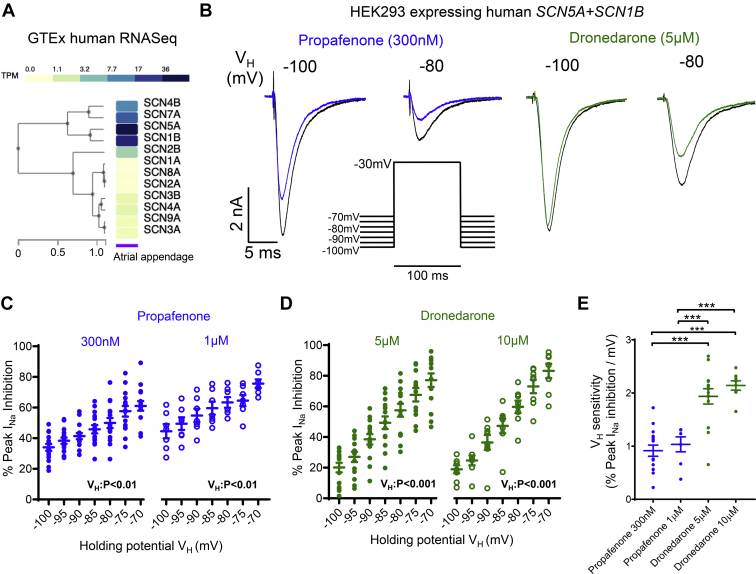
Figure 1.
Human NaV1.5 sodium current (INa) inhibition by propafenone and dronedarone is enhanced at more positive resting membrane potentials (RMPs). A: Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) data showing relative mean expression of sodium channel genes in human atrial appendage (N = 429 samples). B: Inhibition of INa caused by propafenone (300 nM) and dronedarone (5 μM) at 2 different resting membrane potentials/holding potentials (RMP/VH). C, D: Effect of RMP/VH on INa inhibition by propafenone at 300 nM (N = 15 cells) and 1 μM (N = 8 cells), and dronedarone at 5 μM (N = 14 cells) and 10 μM (N = 8 cells). Data are given as mean ± SEM, 1-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). E: RMP/VH sensitivities of propafenone and dronedarone. ∗∗∗P <.001, 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc analysis.