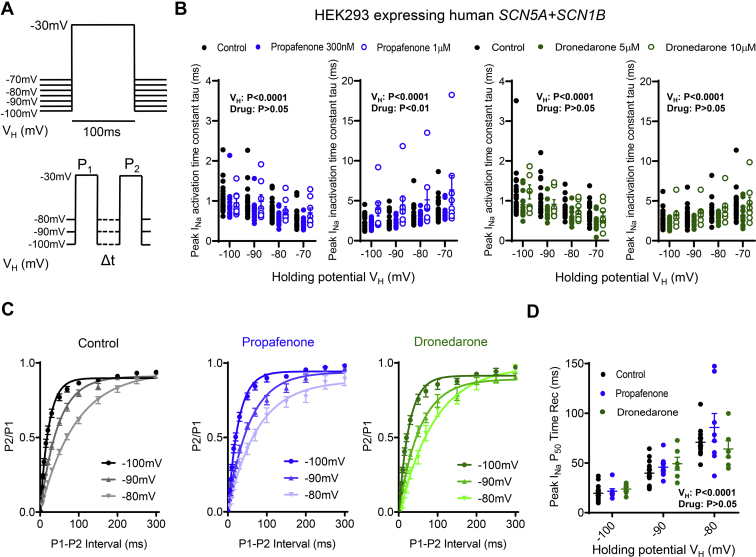
Figure 2.
Human NaV1.5 sodium current (INa) activation, inactivation, and time-dependent recovery kinetics are sensitive to changes in resting membrane potential (RMP). A: Protocols used to measure INa activation/inactivation time kinetics (top) and time-dependent recovery (bottom). B: Activation and inactivation time constants (tau) measured at different resting membrane potentials/holding potentials (RMP/VH) for control, propafenone (300 nM and 1 μM; N = 23 cells total), and dronedarone (5 μM and 10 μM; N = 21 cells total). One-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). C: INa time-dependent recovery measured in control cells (N = 14 cells), propafenone-treated cells (300 nM; N = 8 cells), and dronedarone-treated (5 μM; N = 6 cells). D: Effect of RMP/VH on mean 50% INa recovery times (P50) for all 3 groups. Data are given as mean ± SEM, 2-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc analysis.