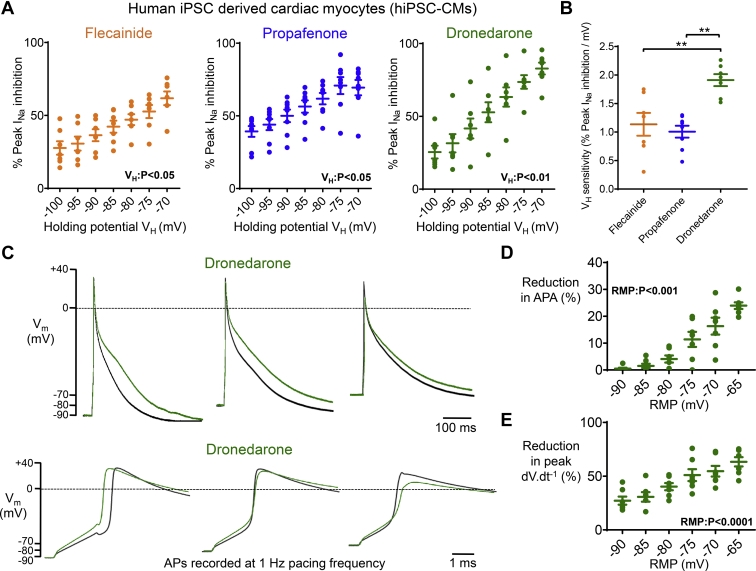
Figure 4.
Dronedarone causes greater inhibition of cardiac action potential amplitude (APA) and upstroke velocity at more positive resting membrane potentials (RMPs). A: Data from human-induced pluripotent stem cells–derived cardiac myocytes (hiPSC-CMs) demonstrating the effect of resting membrane potential/holding potential (RMP/VH) on sodium current (INa) inhibition by flecainide (1 μM; N = 7 cells), propafenone (300 nM; N = 8 cells) and dronedarone (5 μM; N = 7 cells). B: RMP/VH sensitivities of flecainide, propafenone, and dronedarone. ∗∗P <.01, 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni post hoc analysis. C: Action potentials (APs) measured at 3 different RMPs (–100, –90, and –70 mV) measured in a single hiPSC-CM ± dronedarone (5 μM), paced at 1 Hz. D, E: Mean data from hiPSC-CMs (N = 7 cells). Data are given as mean ± SEM, 1-way repeated measures ANOVA.