Figure 6.
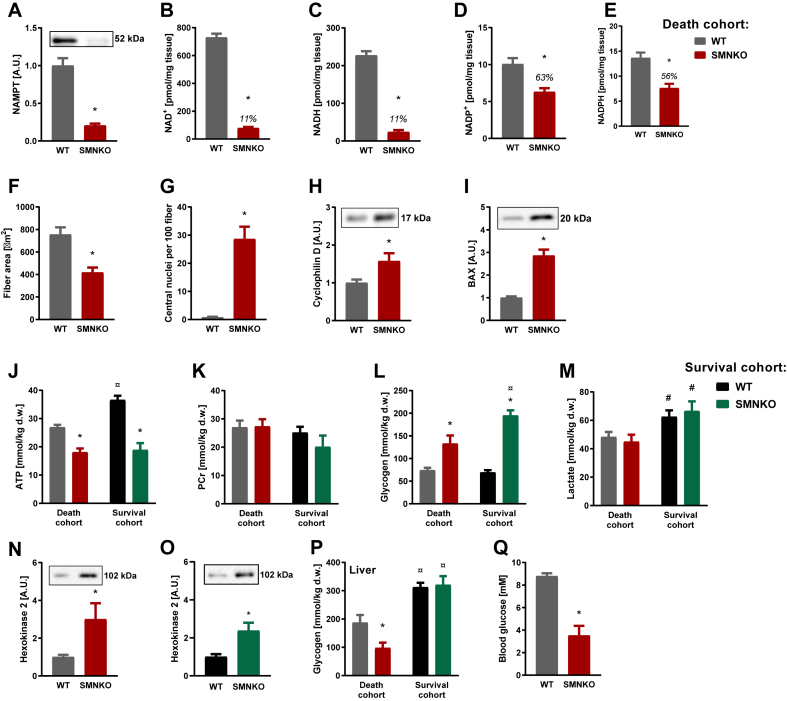
Dying SMNKO mice suffer from whole-body energy depletion.A-C) NAMPT (A), NAD+ (B), and NADH (C) levels in gastrocnemius muscle of WT and SMNKO mice sacrificed just before natural death of the SMNKO mice (4–11 weeks of age, n = 15). D and E) NADP+ (D) and NADPH (E) levels in gastrocnemius muscle of WT and SMNKO mice sacrificed just before natural death of the SMNKO mice (4–11 weeks of age, n = 15). F and G) Average fiber area (F) and number of central nuclei (G) in quadriceps muscle of WT and SMNKO mice sacrificed just before natural death of the SMNKO mice (4–11 weeks of age, n = 15). H and I) CYPD (H) and BAX (I) protein levels in gastrocnemius muscle of WT and SMNKO mice sacrificed just before natural death of the SMNKO mice (4–11 weeks of age, n = 15). J and K) ATP (J) and phosphocreatine (PCr) (K) levels in tibialis anterior (TA) muscle of WT and SMNKO mice sacrificed just before natural death of the SMNKO mice (Death cohort, 4–11 weeks of age, n = 15), and in male WT and SMNKO mice (Survival cohort, 9–14 weeks of age, n = 8–13). L and M) Glycogen (L) and lactate (M) levels in TA muscle of WT and SMNKO mice sacrificed just before natural death of the SMNKO mice (Death cohort, 4–11 weeks of age, n = 15), and in male WT and SMNKO mice (Survival cohort, 9–14 weeks of age, n = 8–13). N and O) Hexokinase 2 protein levels in gastrocnemius muscle of (N) 4–11 weeks of age WT and SMNKO mice sacrificed just before natural death of the SMNKO mice (n = 15), and (O) 9–14 weeks of age male WT and SMNKO mice (n = 8–13). P) Glycogen levels in liver of WT and SMNKO mice sacrificed just before natural death of the SMNKO mice (Death cohort, 4–11 weeks of age, n = 15), and in male WT and SMNKO mice (Survival cohort, 9–14 weeks of age, n = 8–13). Q) Blood glucose levels of WT and SMNKO mice sacrificed just before natural death of the SMNKO mice (4–11 weeks of age, n = 15). Error bars represent SEM. ∗ Difference to WT mice in the same cohort. # Main effect of cohort. ¤ Difference to mice of the same genotype in the other cohort.