Figure 6.
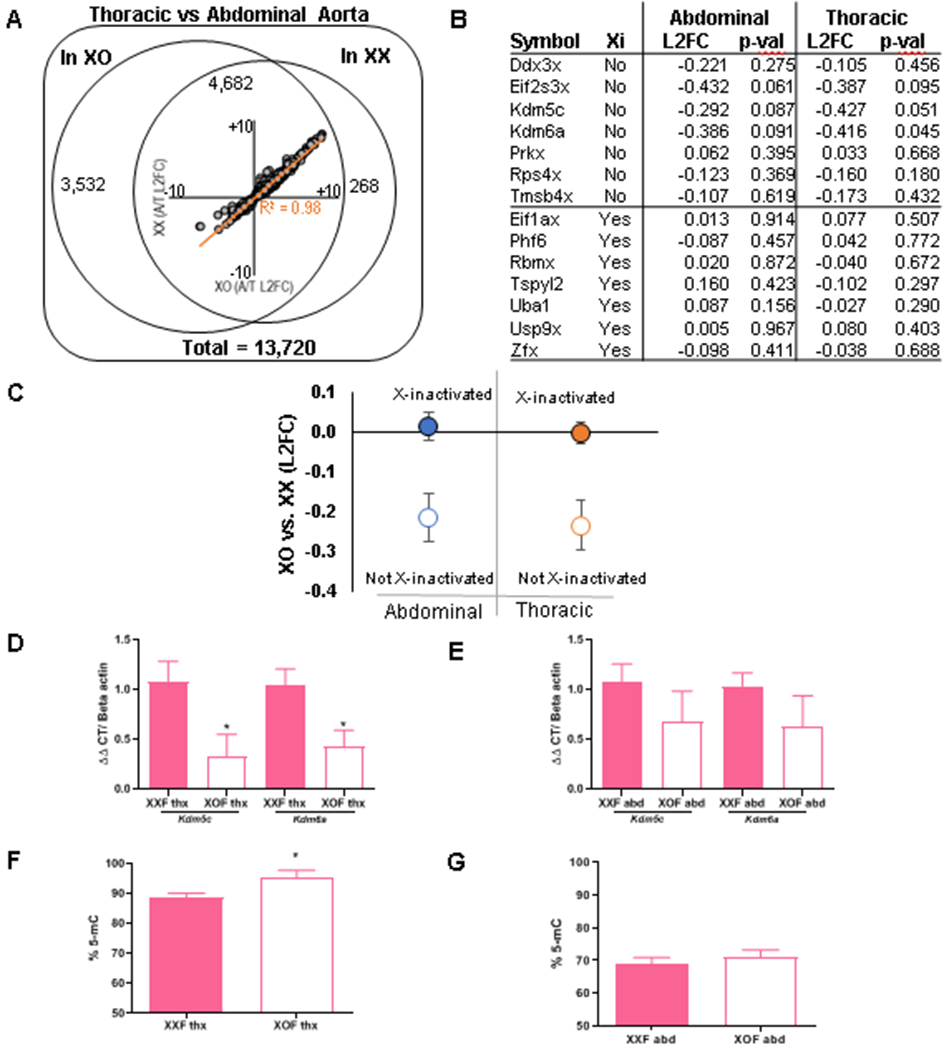
Genes escaping X-inactivation and percent DNA methylation within aortic regions of XXF and XOF Ldlr−/− mice. A-E, Mice were fed a Western diet for one week prior to RNA seq on thoracic and abdominal aortas. A) A total of 13,270 mRNA species annotated to protein-coding genes, of which 8,214 gene transcripts varied between thoracic and abdominal aortas of both sex chromosome genotypes. Of these, 4,950 genes differed between abdominal and thoracic aortas of XXF, and 4,682 of these genes also differed between aortic regions of XOF mice, resulting in large directional agreement and a high correlation between transcripts varying across aortic regions of both genotypes (inset). B) We analyzed 7 genes that either escape or do not escape X-inactivation in aortic regions from each genotype. C, In aggregate, X-inactivated genes (filled circles) show no detectable difference in expression, while genes escaping X inactivation (hollow circles) show significantly decreased expression in abdominal (p = 0.024) and thoracic (p = 0.016) aortas of XOF than XXF mice. D,E) mRNA abundance of Kdm5c and Kdm6a in thoracic and abdominal aortas, respectively. F,G) Percent DNA methylation (% 5-mC) of thoracic and abdominal aortas, respectively, of mice infused with AngII for 3 days. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 5-8 mice/genotype. *, P<0.05 compared to XXF.
