Figure 4.
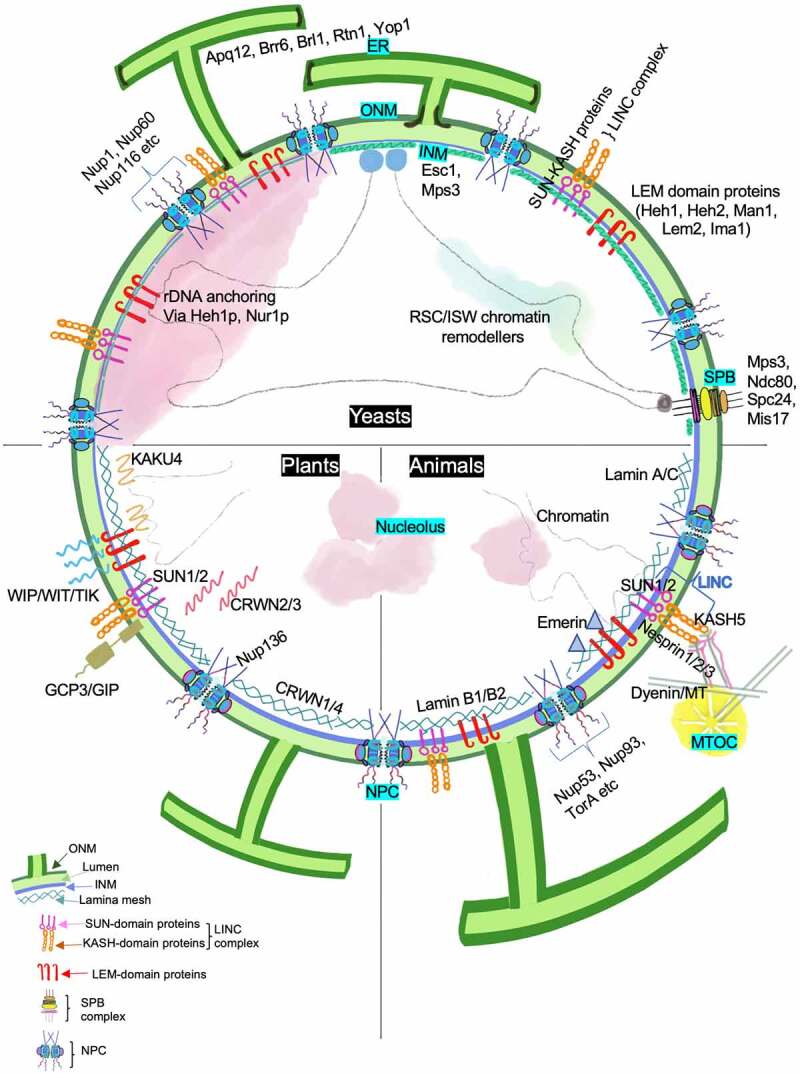
Factors contributing to the maintenance of nuclear shape. The figure summarizes various components that contribute toward regulation of nuclear shape in yeast, plants and animals. Proteins that play a critical role are marked along the associated nuclear sub-compartment and associated organelle. The NE is a double membrane lipid bilayer. The INM has a protein composition that differs from the ONM, with the latter being continuous with ER. Proteins at the INM associate with chromatin and this DNA-protein interaction contributes to overall nuclear stability. Other conserved nuclear compartments are chromosomal territories, nucleolus, telomeric foci and NPCs. In yeast, the SPB complex is INM associated and diametrically opposite to the nucleolus unlike the cytosolic MTOC in animals and plants. Nucleolus is also found at the nuclear periphery in yeast where INM proteins Heh1 and Nur1 anchor the rDNA. On the other hand, the nucleolus in plants and animal cells is away from nuclear periphery, in one or multiple spots
