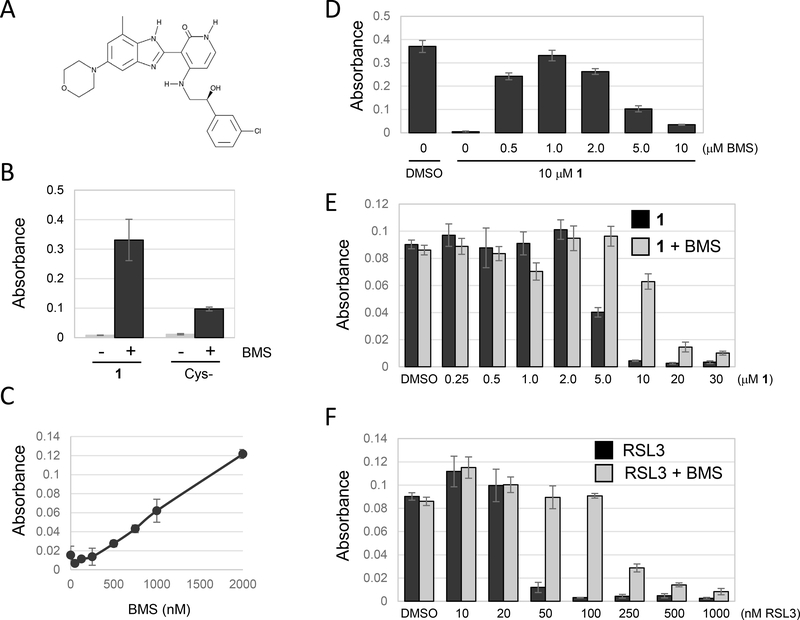
Figure 2.
BMS536924 protects from ferroptotic cell death. Unless otherwise indicated, cell viability was determined using methylene blue staining followed by quantification of absorbance at 668nm. (A) The structure of BMS536924. (B) Effect of BMS536924 on ferroptosis. NCI-H522 cells were plated in DMEM+10% FBS. Twenty four hours later, the media were replaced with cystine-free DMEM containing dialyzed FBS to induce ferroptosis. Alternatively, ferroptosis was induced by leaving cells in DMEM+10% FBS and then exposing to compound 1. Viability in the presence or absence of BMS536924 (BMS) was assessed 24 hours later. (C) Ferroptosis protection by BMS536924 is dose dependent. Ferroptosis was induced by incubating NCI-H522 cells in cystine-free medium for 24 hours. BMS536924 was added at the concentrations indicated and viability determined. (D) Maximal protection of ferroptosis induced by compound 1 occurs at 1 μM BMS536924. NCI-H522 cells were exposed to the compounds indicated and viability determined 72 hours later. (E and F) BMS536924 rescues from both Type I (compound 1) and Type II (RSL3) inducers of ferroptosis. NCI H522 cells were exposed to the compounds indicated and viability determined 72 hours later.