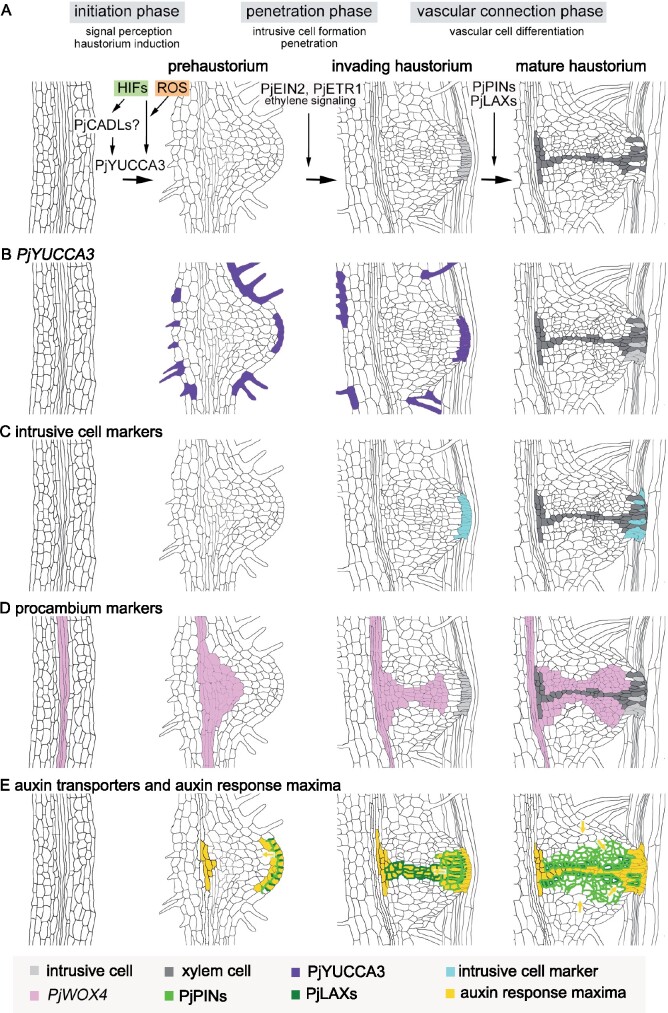
Figure 1.
Developmental stages of a facultative parasite haustorium. A, A schematic diagram of the three phases of haustorium formation. Signals and genes involved in each developmental phase are indicated in the figure. Quinone-type HIFs may be perceived by the orthologs of Arabidopsis CARD1 (CANNOT RESPOND TO DMBQ 1), named CARD-like proteins (CADLs), which drive expression of the auxin biosynthesis gene YUCCA3 (YUCCA-flavin monooxygenase 3) at the tip of the prehaustorium. During the host invasion stage, ethylene signaling driven by ETR1 and EIN2 is required. Directional localization of the auxin efflux transporter PIN (PIN-FORMED auxin transporter family proteins) and the auxin influx transporter LAX (LIKE-AUX1 transporter family proteins) define auxin flow at the center of haustoria where xylem bridges and plate xylem develop. B–E, Schematic diagrams of the expression patterns of select genes during haustorium development. B, Expression patterns (purple) of the auxin biosynthesis gene PjYUCCA3. C, Expression patterns (aqua) of intrusive cell marker genes. D, Expression patterns (pink) of procambium marker genes. E, Expression patterns of auxin transporters and local auxin maxima. Areas highlighted in yellow indicate the sites of localized auxin responses, and yellow arrows indicate direction of auxin flow. Dark and light green lines indicate the localization sites for the auxin transporters PIN and LAX, respectively