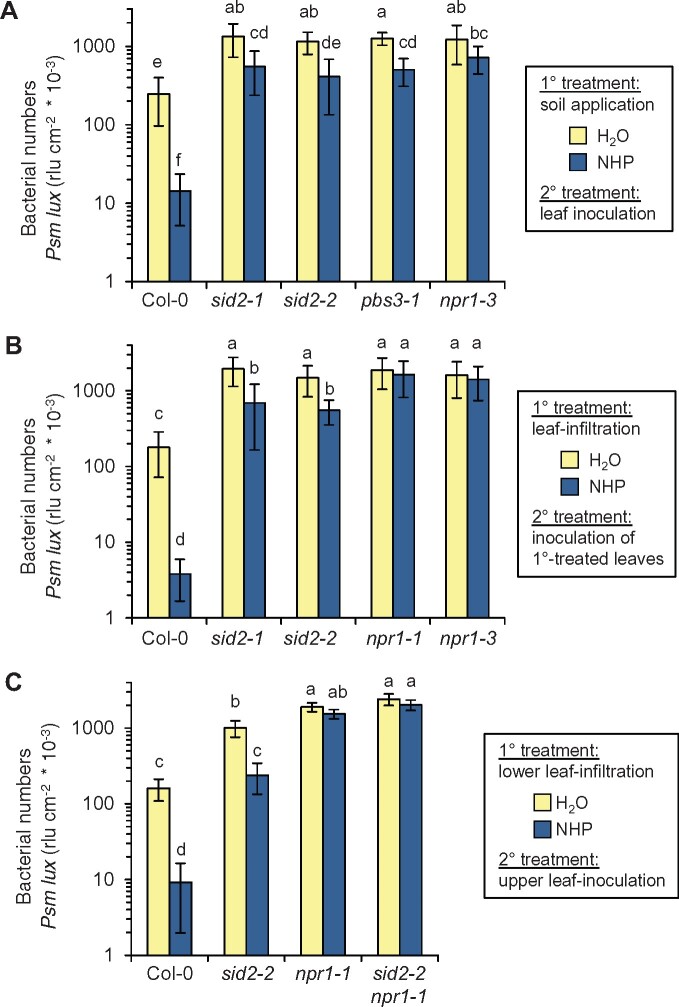
Figure 1.
Arabidopsis SAR against P. syringae triggered by exogenous NHP is modest in the absence of inducible SA biosynthesis and requires NPR1. A, Individual Arabidopsis plants were supplied with 10 mL of an aqueous 1 mM NHP solution or with 10 mL of H2O via the cultivation soil (1° treatment). Three leaves of a plant were inoculated 1 d later with the bioluminescent Psm lux strain (OD600 = 0.001; 2° treatment). Bacterial numbers were determined at 2.5 dpi and expressed as rlus/cm2 leaf area (Hartmann et al., 2018). Bars indicate the mean ± sd of at least 12 biological replicates (n ≥ 12). B, Locally induced acquired resistance by foliar treatment with exogenous NHP. Three leaves of a plant were syringe-infiltrated with NHP solution (1 mM) or H2O (1° treatment). One day later, the same leaves were inoculated with Psm lux and bacterial numbers quantified at 2.5 dpi. Bars indicate the mean ± sd of at least 16 biological replicates (n ≥ 16). C, SAR by foliar treatment with exogenous NHP. Three lower leaves of a plant were syringe-infiltrated with 1 mM NHP or H2O (1° treatment). One day later, three upper, distant leaves were inoculated with Psm lux and bacterial numbers quantified at 2.5 dpi. Bars indicate the mean ± sd of at least nine biological replicates (n ≥ 9). Different letters denote significant differences (P < 0.05, ANOVA and post hoc Tukey’s HSD test). Assessment of bacterial numbers in leaves 2 h after inoculation with Psm lux for the experimental settings of A–C is depicted in Supplemental Figure S1.