Fig. 1. Production of nanomice.
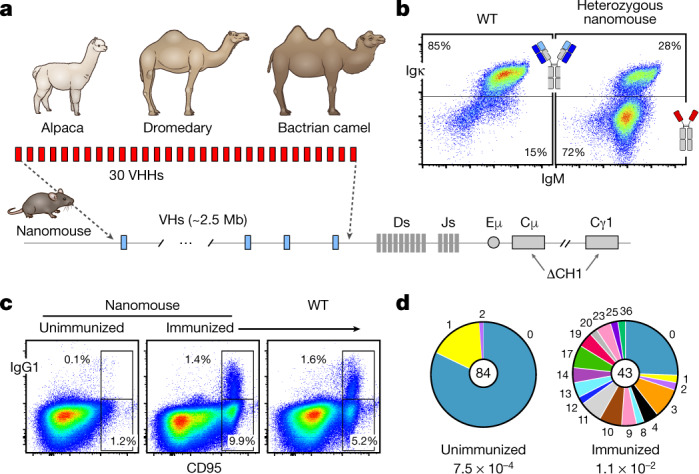
a, Thirty VHHs selected from alpaca, dromedary and Bactrian camel were inserted via CRISPR–Cas9 in lieu of the 2.5-Mb mouse VH locus. CH1 exons from Cμ and Cγ1 were also deleted to avoid misfolding of the antibody heavy chain. b, Flow cytometry analysis of splenic B220+ B cells from wild-type (WT) mice or heterozygous nanomice. IgM+Igκ+ cells express conventional heavy–light chain antibodies, whereas IgM+Igκ− cells are mostly Igλ+ in wild-type mice (not shown) or single-chain-antibody B cells in nanomice. c, Flow cytometry analysis of splenic cells from unimmunized and immunized nanomice and controls stained with CD95 and IgG1. d, Pie charts showing VHH somatic hypermutation in unimmunized and immunized nanomice. Pie segments are proportional to the VHH sequences carrying the mutations indicated on the periphery of the chart. The middle circle shows the total number of sequences, and mutation frequency is given below.
