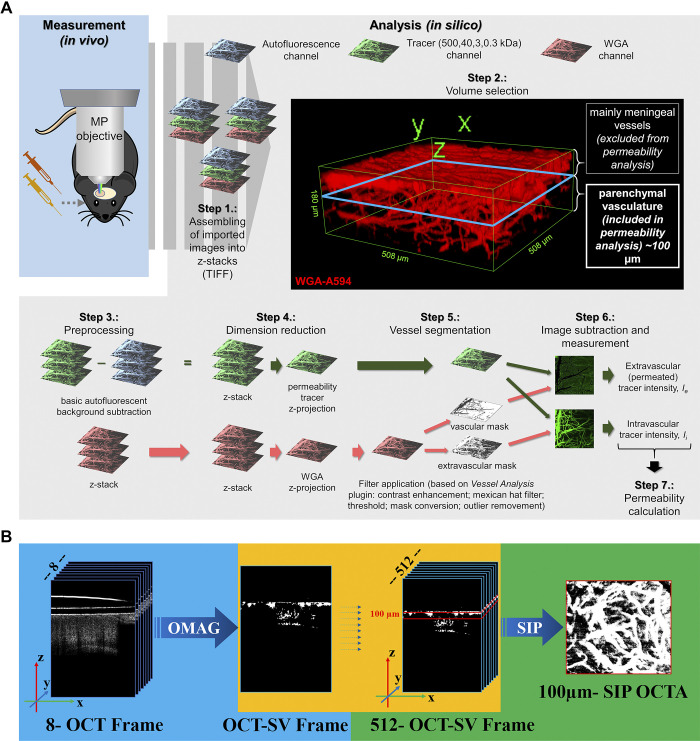
Figure 2.
Computational workflows for in silico analysis of two-photon microscopy and optical coherence tomography (OCT) images. A: computational workflow for in silico analysis of two-photon microscopy images for blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability quantification with image subtraction analysis method. After in vivo measurement, the recorded images were exported in TIFF format and assembled into z-stacks. 3-D reconstruction of an example stack is presented in Step 2. For quantification an ∼100-μm-thick cortical volume was used in 50–150 μm depth from the “0 level” of the meningeal vessels to avoid quantification of images derived from nonparenchymal layers. After elimination of autofluorescent background and dimension reduction, filters were applied on wheat germ agglutinin (WGA)-Alexa 594 (WGA-A594) channel only to obtain vasculature as a segmented binary mask. Binary masks were then qualitatively subtracted from tracer channel images, and the resulting extravascular and intravascular intensity images were measured. Data gained from image analysis were used for permeability calculation. B: OCT image analysis. Original z-stacks were assembled and calculated with average decorrelation in OCT speckle variance frames.