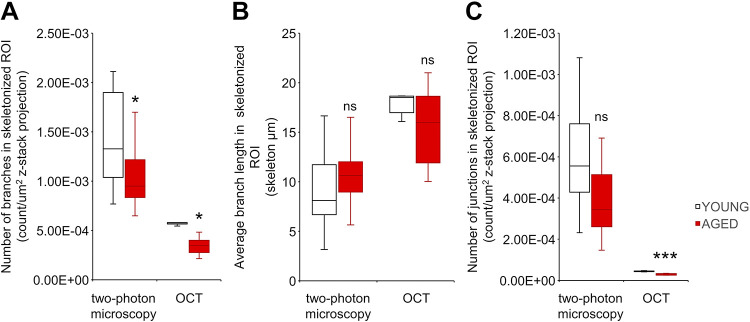
Figure 4.
Comparison of two-photon and optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging-based indexes relevant for age-related cerebromicrovascular rarefaction. To evaluate the usefulness of additional imaging-based indexes relevant for age-related cerebromicrovascular rarefaction in mice, branching patterns on skeletonized images were analyzed. Comparison of indexes representing number of branches (MP: P = 0.038, n = 25/20; OCT: P = 0.008, n = 5/5) (A) and number of junctions (MP: P = 0.06, n = 25/20; OCT: P = 0.00023, n = 5/5) (C) showed significant age-related declines. In contrast, the index representing average branch lengths (MP: P = 0.34, n = 25/20; OCT: P = 0.58, n = 5/5) (B) did not differ between the two groups. Data are presented as interquartile distributions with median. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with young group.