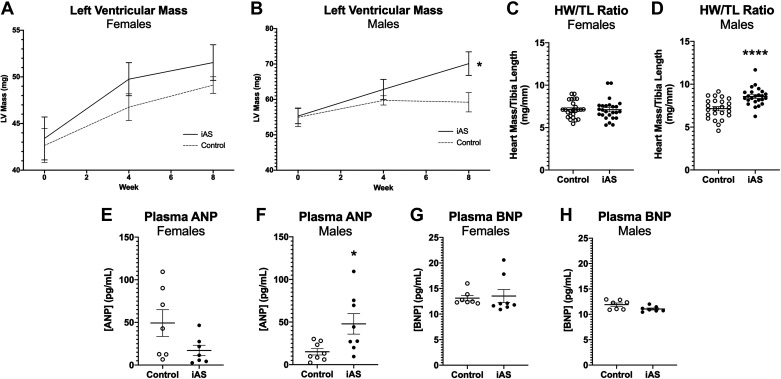
Figure 2.
Exposure to inorganic arsenic (iAS) induces sex-dependent hypertrophy of the heart. Left ventricular mass (LV mass) extrapolated from transthoracic echocardiography in females (A) and males (B) (*P = 0.0149 vs. control, two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons) at 0, 4, and 8 wk of exposure (n = 9-10 mice/group). Heart mass normalized to tibia length (HW/TL) in females (C) and males (D) (****P < 0.0001 vs. control; n = 24-25 hearts/group). Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) in females (E) and males (F) (*P = 0.0379 vs. control; n = 9-10 mice/group). Plasma brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) in females (G) and males (H) (n = 9-10 mice/group). Outliers were determined by the ROUT method (Q = 1%), and significance was determined by Mann–Whitney test.