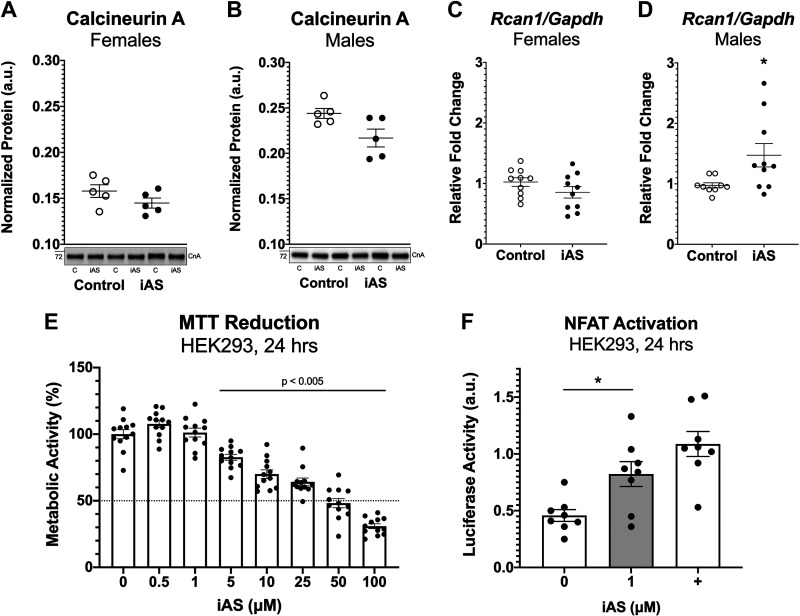
Figure 6.
Exposure to inorganic arsenic (iAS) may activate the calcineurin-nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) signaling pathway. Protein expression of calcineurin A in male (A) and female (B) hearts (n = 5 hearts/group). Protein levels of each target were normalized to total transferred protein levels. Myocardial mRNA transcript levels of regulator of calcineurin 1 (Rcan1) in females (C) and males (D) (*P = 0.0161 vs. control; n = 10 hearts/group). Transcript levels of each target were normalized to Gapdh mRNA expression, which did not change with iAS exposure in either sex. E: MTT reduction in HEK-293 cells treated with varying levels of iAS for 24 h, represented by optical density as a percentage of the average control, following a dose-response curve (P < 0.005 vs. control, ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons, n = 12 wells/group). F: NFAT-luciferase activity in HEK-293 cells transfected with NFAT-luciferase and Renilla-luciferase, as well as Trpc6 as a positive control (+), and treated with 1 μM iAS for 24 h (*P = 0.0214 vs. control; n = 8 wells/group). NFAT firefly luminescence was normalized to Renilla luminescence. Outliers were determined by the ROUT method (Q = 1%), and significance was determined by Mann–Whitney test.