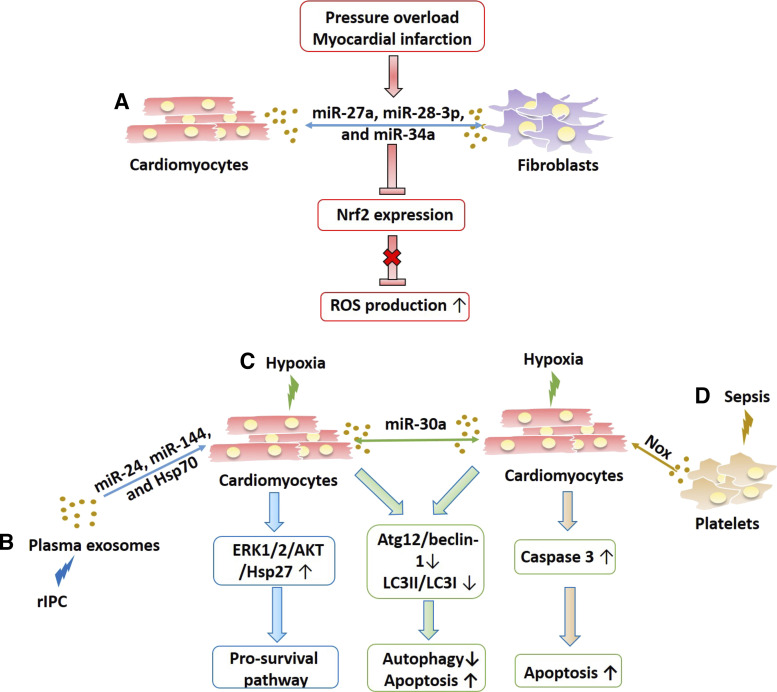
Figure 5.
The roles of exosomes in the antioxidant and apoptotic signaling pathways. A: exosome shuttling between cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts containing various miRNAs such as miR027a, miR-28-3p, and miR-34a can be attributable to reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction during cardiac diseases such as pressure overload and myocardial infarction by repressing Nrf2 expression, an antioxidant arm. B: in remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC), plasma-derived exosomes can protect cardiomyocytes against apoptosis by increasing ERK1/2/Akt/Hsp27 to promote activation of prosurvival pathways. In contrast, exosomes from cardiomyocytes subjected to hypoxia (C) contain miR-30a and can cross-talk between other cardiomyocytes to decrease the autophagy response and increase apoptosis. D: platelet-derived exosomes can also induce apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by increasing caspase-3 activity to increase apoptosis.