Figure 3:
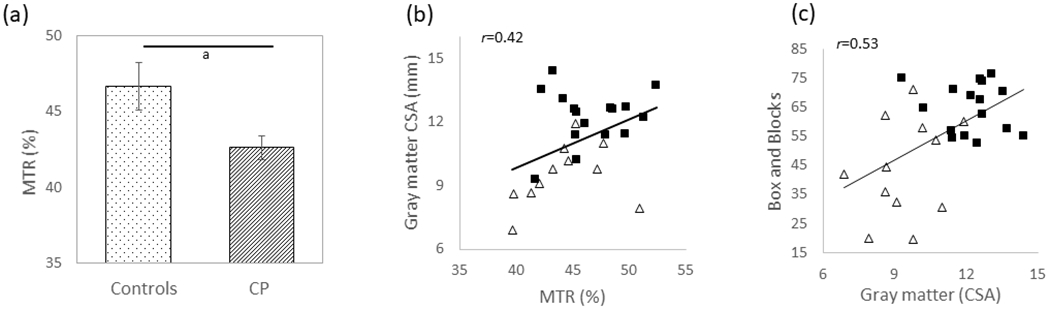
(a) The magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) in the corticospinal tracts for the adults with cerebral palsy (CP) and population norm adult controls. The adults with CP had significantly lower MTR in the corticospinal tracts, suggesting greater microstructural disruptions. (b) Scatter plot depicting the positive relationship between the corticospinal tract MTR and gray matter cross-sectional area (CSA). Adults with CP are depicted with white triangles, and the adult controls are depicted with black squares. Less gray matter was associated with a reduction in the corticospinal tract MTR, suggesting that participants with less grey matter CSA tended to have greater damage to the corticospinal tract microstructure. ap≤0.05. (c) Scatter plot depicting the relationship between the gray matter CSA and Box and Block Test scores. More gray matter was associated with improved hand dexterity.
