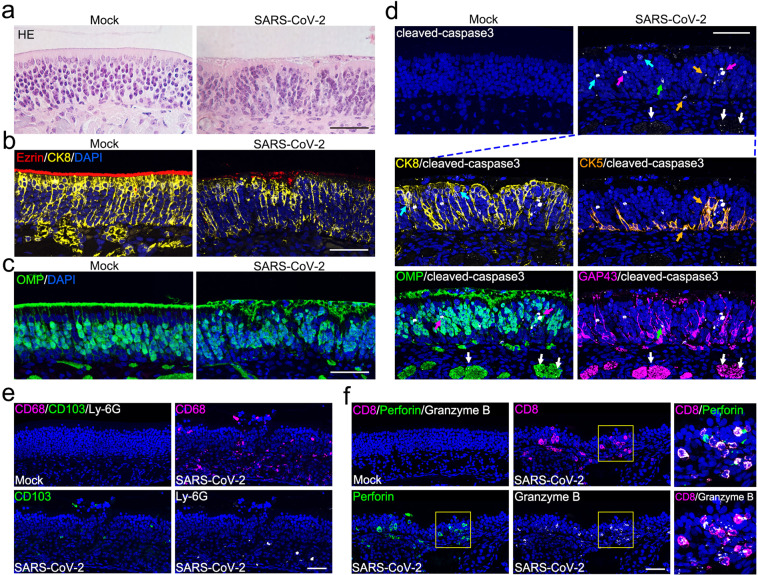
Fig. 3. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces apoptosis and immune cell infiltration in the OE.
a Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining results showing histopathological changes of the OE. b Representative results of multiplex immunofluorescent detection of sustentacular cells (CK8 positive) and microvilli (Ezrin positive) of the OE. c Representative results of immunofluorescent detection of mOSNs (OMP positive) of the OE. d Apoptosis of olfactory epithelial cells (cleaved-caspase3 positive, white) after SARS-CoV-2 infection. The panels below show apoptosis of sustentacular cells (CK8 positive, yellow; indicated by cyan arrows), HBCs (CK5 positive, gold; indicated by gold arrows), mOSNs (OMP positive, green; indicated by magenta arrows), iOSN (GAP43 positive, magenta; indicated by green arrows), and olfactory nerve bundles (OMP/GAP43 positive; indicated by white arrows). e Representative multiplex immunofluorescent staining results showing infiltration of macrophages (CD68 positive, magenta), dendritic cells (CD103 positive, green), and neutrophils (Ly-6G positive, white) in the OE after infection. f Representative multiplex immunofluorescent staining results showing infiltration of CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocytes (magenta) with expression of perforin (green) and granzyme B (white) in the olfactory mucosa after infection. The framed areas are shown adjacently at larger magnifications. Scale bar, 50 μm.