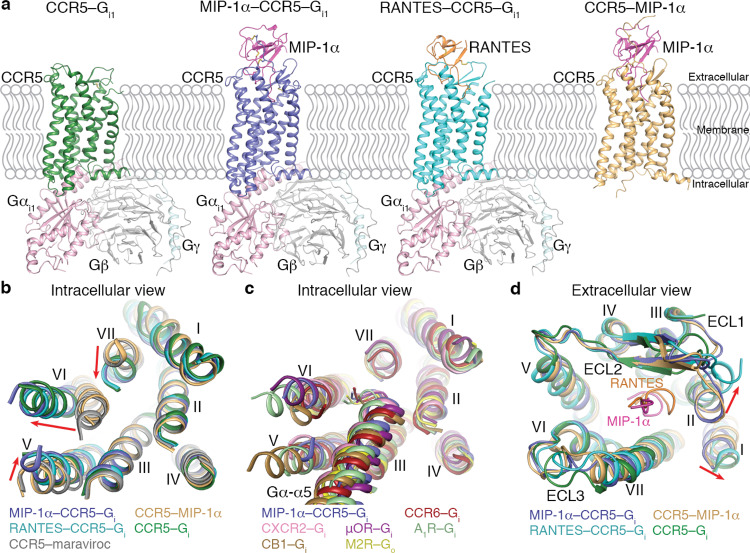
Fig. 1. Overall structures of the CCR5–chemokine and CCR5–Gi1 complexes.
a Cryo-EM structures of CCR5–Gi1, MIP-1α–CCR5–Gi1, and RANTES–CCR5–Gi1 and crystal structure of CCR5–MIP-1α. The structures are shown in cartoon representation. The receptor CCR5 in the four structures is colored green, blue, cyan, and gold, respectively. The chemokines MIP-1α and RANTES are colored magenta and orange, respectively. The three subunits in Gi1 are colored light pink, light gray, and light cyan, respectively. Disulfide bonds are shown as yellow sticks. b Comparison of the transmembrane helical bundle conformation in the CCR5 structures. The helical bundles in the structures of CCR5–Gi1, MIP-1α–CCR5–Gi1, RANTES–CCR5–Gi1, and CCR5–MIP-1α and the previously determined structure of CCR5–maraviroc (PDB ID: 4MBS) are colored green, blue, cyan, gold, and gray, respectively. The red arrows indicate the movements of the intracellular tips of helices V, VI, and VII in the Gi1-bound CCR5 structures compared to those in the structures of CCR5–MIP-1α and CCR5–maraviroc. c Comparison of the G protein-binding pocket in the structures of MIP-1α–CCR5–Gi1 and other class A GPCR–Gi/o complexes. The helical bundles and the C termini of Gα α5-helix in the MIP-1α–CCR5–Gi1 structure and the structures of CCR6–Gi, CXCR2–Gi, μOR–Gi, A1R–Gi, CB1–Gi, and M2R–Go (PDB IDs: 6WWZ, 6LFO, 6DDE, 6D9H, 6N4B, and 6OIK) are colored blue, dark red, pink, purple, light green, brown, and yellow, respectively. d Comparison of the extracellular regions in the structures of CCR5–Gi1, MIP-1α–CCR5–Gi1, RANTES–CCR5–Gi1, and CCR5–MIP-1α. The N-terminal regions in MIP-1α and RANTES (residues 1–9) are shown in cartoon representation and colored magenta and orange, respectively. The red arrows indicate movements of the extracellular tips of helices I and II in the RANTES–CCR5–Gi1 structure compared to those in the MIP-1α-bound structures.