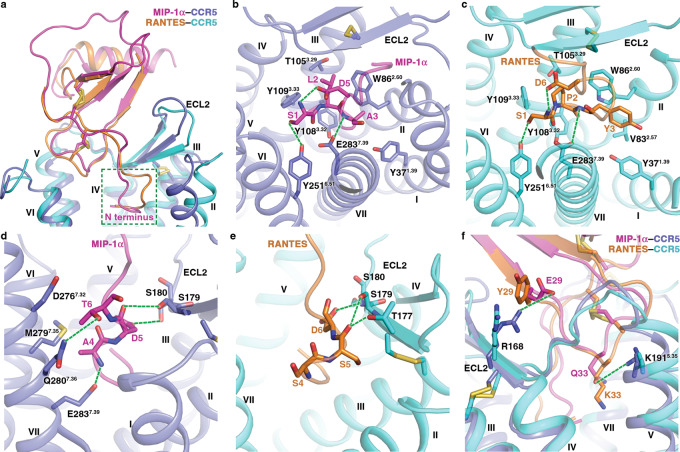
Fig. 3. Binding modes of MIP-1α and RANTES in CRS2.
a Comparison of the binding poses of MIP-1α and RANTES in CCR5. The structures of MIP-1α–CCR5–Gi1 and RANTES–CCR5–Gi1 are shown in cartoon representation and colored blue (CCR5)/magenta (MIP-1α) and cyan (CCR5)/orange (RANTES). The N-terminal regions of the chemokines are highlighted by a green dashed box. b, d Binding mode of the N-terminal residues of MIP-1α. b Binding mode of the MIP-1α residues S1–A3; d binding mode of the MIP-1α residues A4-T6. The MIP-1α–CCR5–Gi1 structure is shown in cartoon representation. The MIP-1α and CCR5 residues that are involved in interactions are shown as sticks with magenta and blue carbons, respectively. The polar interactions are displayed as green dashed lines. c, e Binding mode of the N-terminal residues of RANTES. c Binding mode of the RANTES residues S1–Y3; e binding mode of the RANTES residues S4-D6. The RANTES–CCR5–Gi1 structure is shown in cartoon representation. The RANTES and CCR5 residues that are involved in interactions are shown as sticks with orange and cyan carbons, respectively. The polar interactions are displayed as green dashed lines. f Comparison of interactions formed by the chemokine residues 29 and 33. The structures of MIP-1α–CCR5–Gi1 and RANTES–CCR5–Gi1 are shown in cartoon representation. The MIP-1α residues E29 and Q33 and the CCR5 residues R168 and K1915.35 form polar interactions in the MIP-1α–CCR5–Gi1 structure and the counterparts in the RANTES–CCR5–Gi1 structure are shown as sticks.