Figure 2. The fronto-limbic circuit.
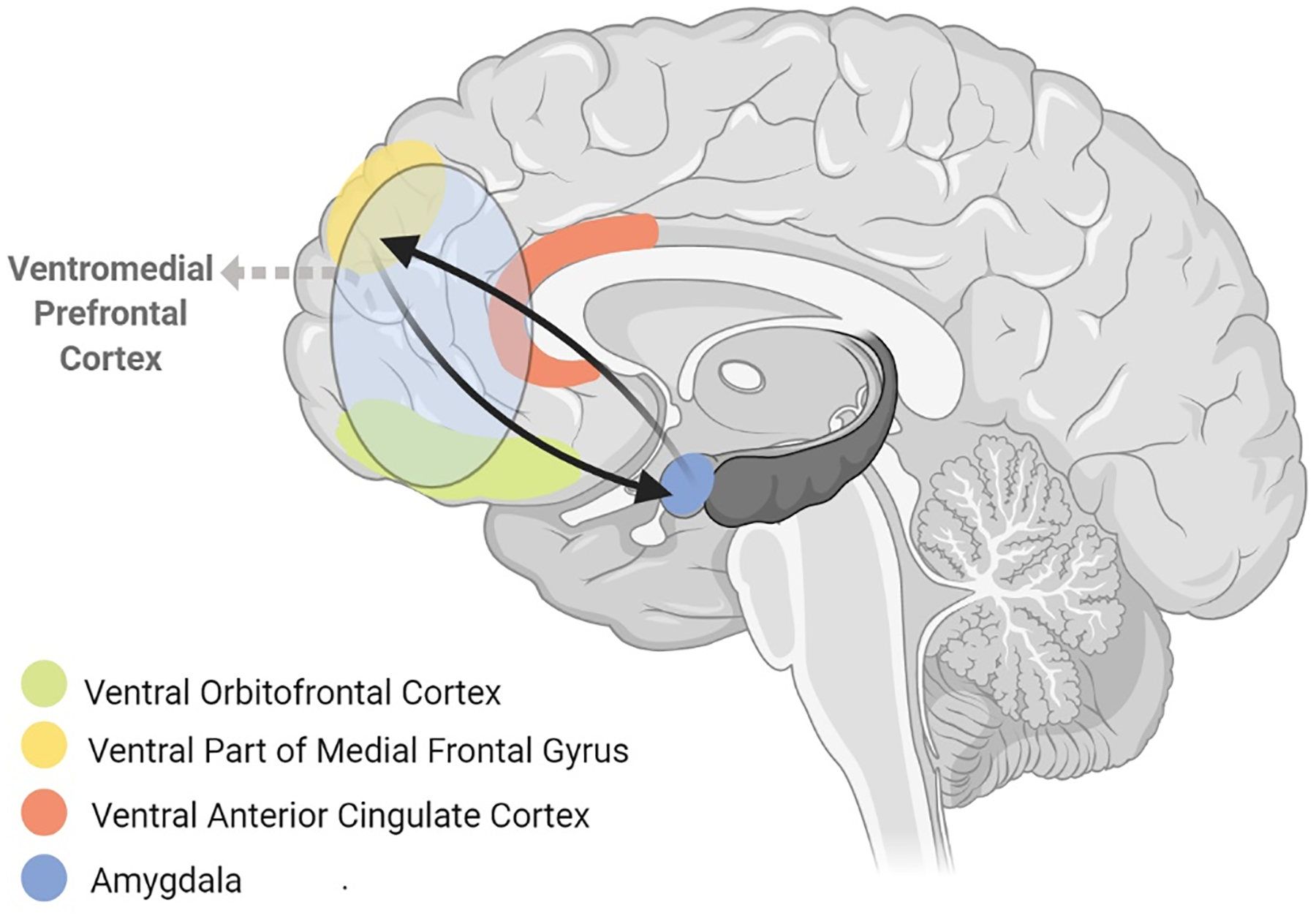
includes the amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC, consisting of ventral orbitofrontal cortex, ventral anterior cingulate cortex and the ventral part of medial frontal gyrus). These regions are structurally and functionally connected with each other to form a network that generates emotional responses (amygdala and NAcc) and evaluates whether those responses are appropriate or require regulation (vmPFC). The fronto-limbic circuit is connected with the hippocampus and regions from other circuits that are involved in top-down behavioral control, including the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) from the dorsal cognitive circuit, and can recruit these regions to dampen fronto-limbic activity thereby facilitating emotional regulation.
