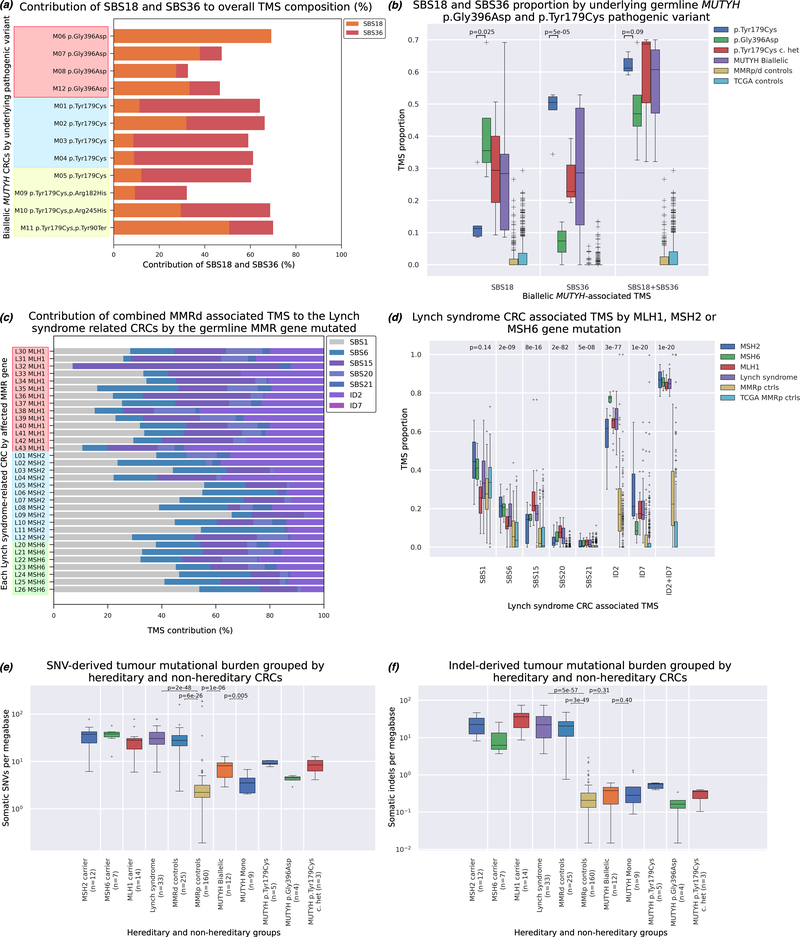
Figure 4.
The investigation of MUTYH pathogenic variant (PV) and MMR gene specific tumour mutational signatures (TMS) profiles: (a) The contribution of the biallelic MUTYH-associated signatures SBS18 and SBS36 to each of the 12 biallelic MUTYH related CRCs by their underlying germline PVs: (i) homozygous p.Gly396Asp carriers, (ii) homozygous p.Tyr179Cys carriers and (iii) compound heterozygous p.Tyr179Cys carriers, (b) The mean±SD of SBS18, SBS36 and combined SBS18/SBS36 by underlying germline MUTYH pathogenic variant carrier group and CRC control groups. P-values indicate difference between CRCs from homozygous p.Gly396Asp carriers and homozygous p.Tyr179Cys carriers, (c) The contribution of the Lynch syndrome-associated TMS identified in our study for each of the 33 CRCs from the MLH1, MSH2 and MSH6 gene pathogenic variant carriers, (d) The distribution of each of the Lynch syndrome-associated TMS across the 14 CRCs from MLH1 carriers, 12 CRCs from MSH2 carriers, and 7 CRCs from the MSH6 carriers and controls groups. P-values indicate differences between the six groups for each individual TMS as measured by ANOVA. (e) Somatic single nucleotide variant (SNV)-derived tumour mutational burden for hereditary and non-hereditary CRCs. CRCs from both biallelic MUTYH carriers and Lynch syndrome carriers exhibited significantly higher SNV-derived mutational burden compared with CRCs from MMRp controls (p=1.1×10−6 and p=2×10−48, respectively; excluding three ultra-hypermutated CRCs related to somatic mutations within the exonuclease domain of POLE), (f) Somatic insertion and deletion (Indel)-derived tumour mutational burden for hereditary and non-hereditary CRCs. CRCs from Lynch syndrome carriers exhibited significantly higher Indel-derived mutational burden compared with CRCs from MMRp controls (p=5×10−57, while CRCs from biallelic MUTYH carriers were not found to have a significant difference in Indel-derived mutational burden compared with CRCs from MMRp controls (p=0.31).