Figure 2.
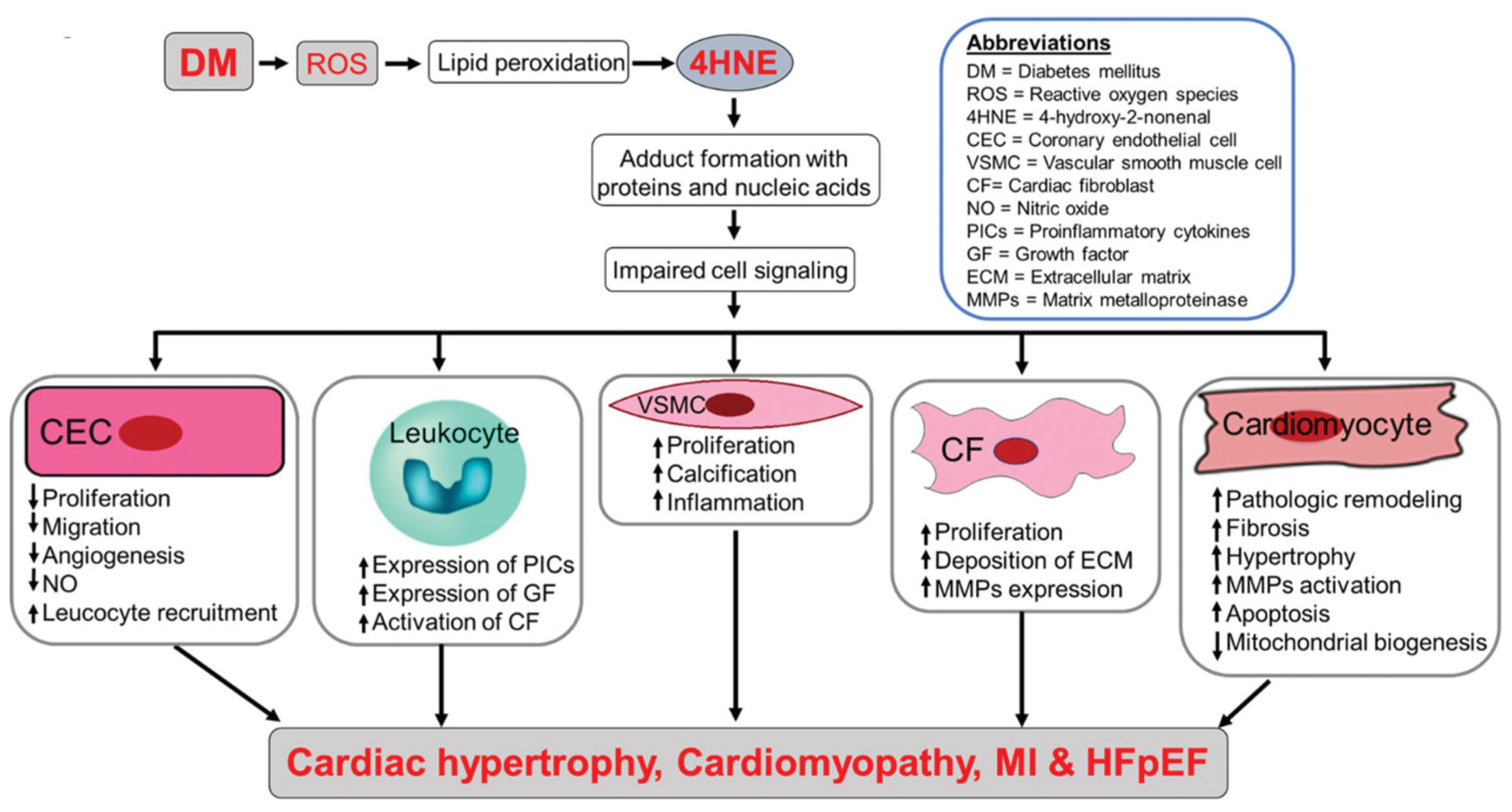
Possible mechanism of diabetes mellitus (DM)-mediated 4-HNE-induced cardiac complications. DM-mediated 4-HNE forms adducts with proteins and nucleic acids which affects the cell signaling of multiple cell types in the heart. Thus, it leads to cellular dysfunction and ultimately cardiac complications such as cardiac hypertrophy, cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. 4-HNE: 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal; CEC: coronary endothelial cell; CF = cardiac fibroblast; ECM: extracellular matrix; GF: growth factor; MMPs: matrix metalloproteinase; NO: nitric oxide; PICs: proinflammatory cytokines; ROS: reactive oxygen species; VSMC: vascular smooth muscle cell.
