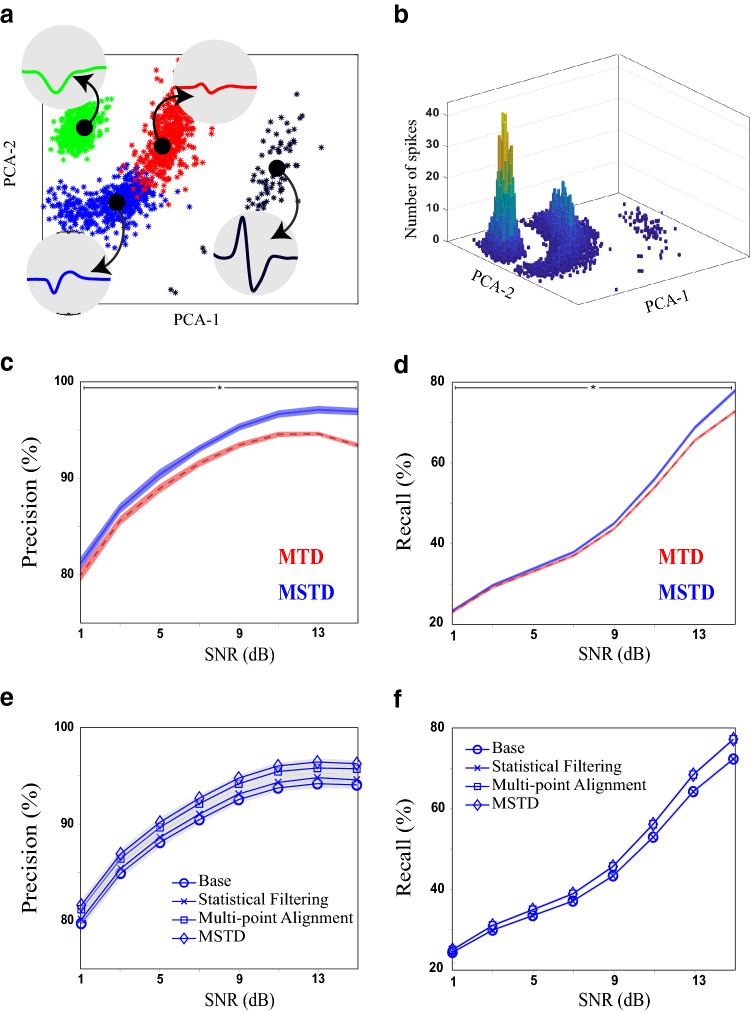
Figure 4.
Evaluating the detection phase of the MSTD algorithm using synthesized dataset35,36 in the detection phase. The dataset contains 200 sessions of 200-s recording with a sampling rate of 40 kHz. (a) A sample session is visualized using its two first principal components. There exist four distinct neurons distinguished by four colors. The average waveform of each neuron is also indicated in a 1.2-ms interval. (b) A sample distribution of spike waveforms. The x and y axes are the first two principal components of waveforms and the z-axis is the frequency of spikes. (c, d) Evaluating the proposed detection (multi-point alignment, and statistical filtering procedures). The precision (c) and recall (d) of MSTD in the detection phase is compared with MTD. The shaded area is the standard deviation. The horizontal line with the star shows where the values differ significantly. (e, f) The effect of statistical filtering and multi-point alignment on detection performance in terms of precision and recall. The MSTD method without any alignment and noise removal is depicted by "Base". The effect of multi-point alignment is higher than statistical filtering. In terms of recall, since statistical filtering only deals with false alarms, it has no effect on the performance.