Figure 6.
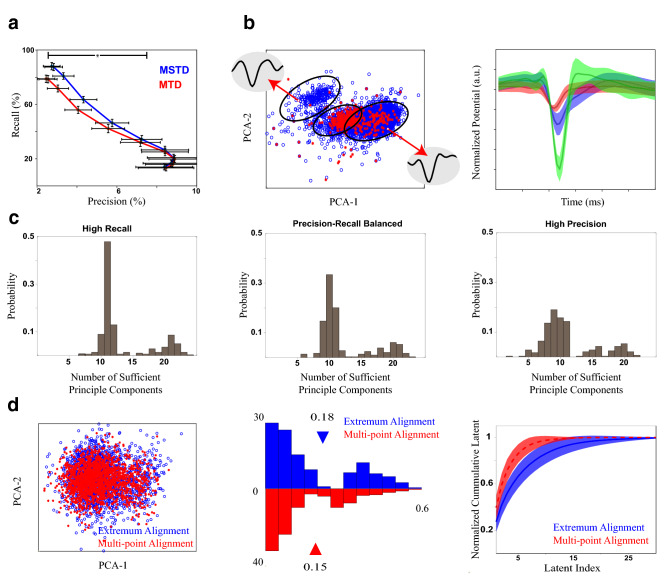
Comparison of MTD and MSTD using the real dataset of simultaneous intracellular and extracellular recordings of rat hippocampus37,49. (a) The precision-recall curve of the detection results. To achieve this curve, the detection threshold is varied proportional to the noise power. The standard deviation of the precision and recall are indicated using horizontal and vertical error bars, respectively. As can be seen, the precision values are small. The horizontal line with the star shows where the values of both recall and precision differ significantly. (b) It shows the reason for small values of precision. A recording sample is visualized using the two first principal components (left). The blue circles show the detected samples, and the red stars show the spikes detected using the ground truth. On the right, the average waveforms of neurons of this sample are illustrated. The clusters are formed using simple manual clustering. The shaded area states the standard deviation. (c) The histogram of the number of principal components is needed to describe the spike waveforms, nc, calculated by Eq. (5), for three situations: high recall (left), which is the point with the most recall value in (a), precision-recall balanced (middle), which is the point in the middle of high recall and high precision points in (a), and high precision (right), which is the point with the most precision value in (a). (d) The effect of alignment on the cluster compactness. A sample of ground truth spikes of two recordings is visualized using the first two principal components (left). The blue circles and red stars show data for two alignment methods. One is the alignment based on waveform extremum (extremum alignment), and the other is the proposed multi-point alignment. The histogram of within distance of ground truth spikes for extremum alignment and the proposed multi-point alignment (middle), and normalized cumulative latent [the left side of Eq. (5)] is shown for both alignment methods (right). The shaded area is the standard deviation.