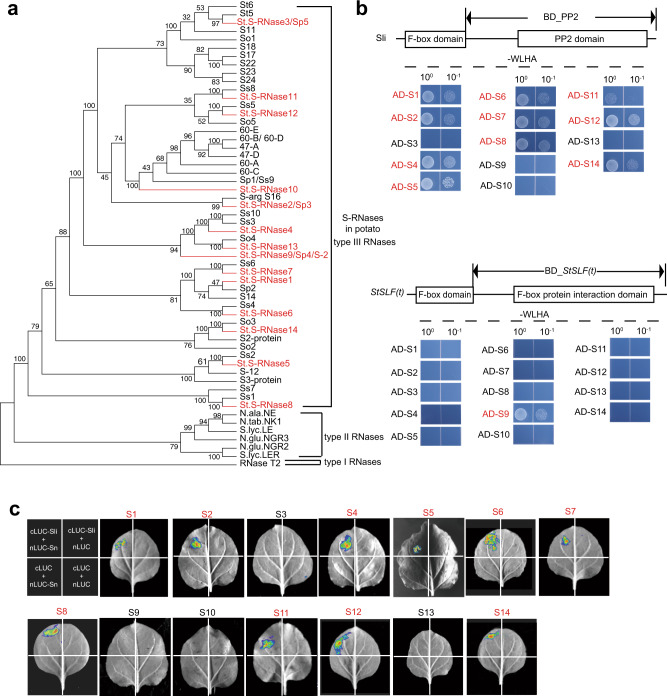
Fig. 3. Wide interactions between Sli and 14 types of potential StS-RNases.
a A phylogenetic tree analysis of the potatoes S-RNases. StS-RNase1–14 are 14 types of S-RNases reported in this study (indicated in red), while the other 35 S-RNases were obtained from GenBank. b Yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) analysis of the interactions between 14 potential S-RNases and the PP2 domain of Sli (BD-PP2). The conserved domains of Sli are indicated by rectangles. The interactions between potential S-RNases and the full length of Sli are shown in Supplementary Fig. 6. The F-box protein interaction domain of a SLF gene (RHC01H2G1617) was used as a negative control [BD-StSLF(t)]. WLHA, synthetic dropout media lacking tryptophan, leucine, histidine, and adenine. BD binding domain, AD activation domain. c The firefly luciferase (LUC) complementation imaging assays of the interactions between the S-RNases and the PP2 domain of Sli. LUC signal was captured in the leaf area co-expressing the PP2 domain of Sli and each of the S-RNases (indicated in red), except for S3, S9, S10, and S13. Sn denote each type of the StS-RNase1–14, nLUC the N terminal of LUC protein, cLUC the C terminal of LUC protein. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results.