Fig 5.
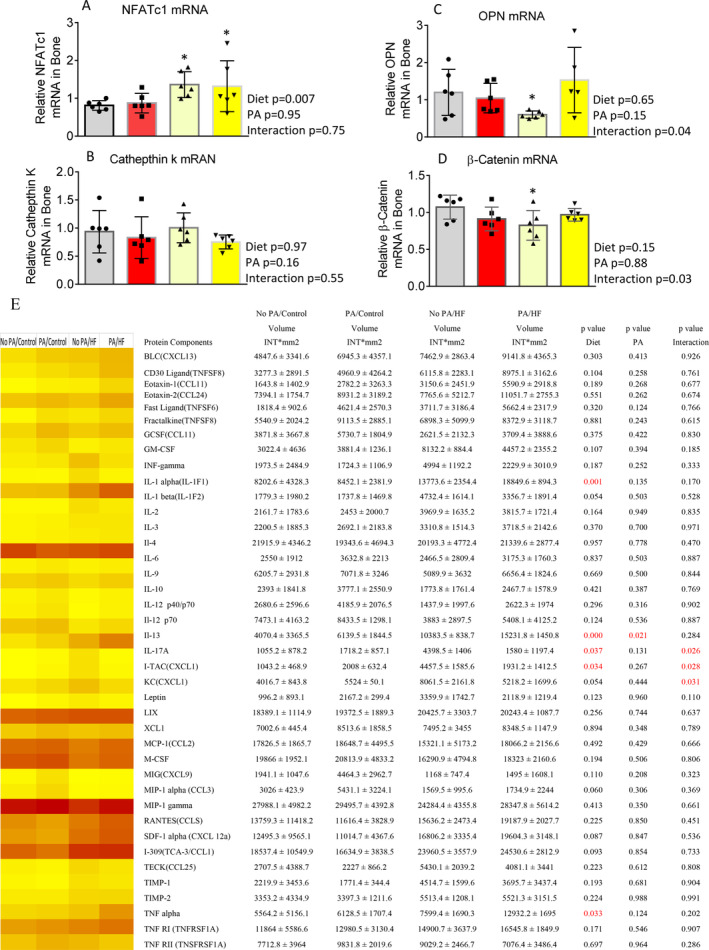
Short‐term early‐life–increased physical activity (PA) via access to voluntary running wheel does not ameliorate high‐fat diet (HFD) bone resorption, it exacerbated HFD‐induced inflammation in bone. (A–D) Real‐time PCR for nuclear factor of activated T‐cells 1 (NFATc1), cathepsin K, osteopontin (OPN), and β‐catenin mRNA expression in total RNA isolated from spine L3 vertebrae from no PA/control, PA/control, no PA/HF, and PA/HF of 16‐month‐old mouse groups. Data were expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6 per group). p Value was analyzed by two‐way ANOVA with a HFD and early‐life PA as the main factors and their interactions. Additionally, *p < 0.05 by t test compared with no PA/control group. (E) Antibody array analysis showing increased inflammatory factor expression in PA/control, no PA/HF, and PA/HF of 16‐month‐old mouse groups in total proteins isolated from spine L3 vertebrae compared with those from no PA/control group, the heat map analysis for comparison of all factors. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. p Value was determined by two‐way ANOVA with a HFD and early‐life PA as the main factors, and their interactions. HF, high fat.
