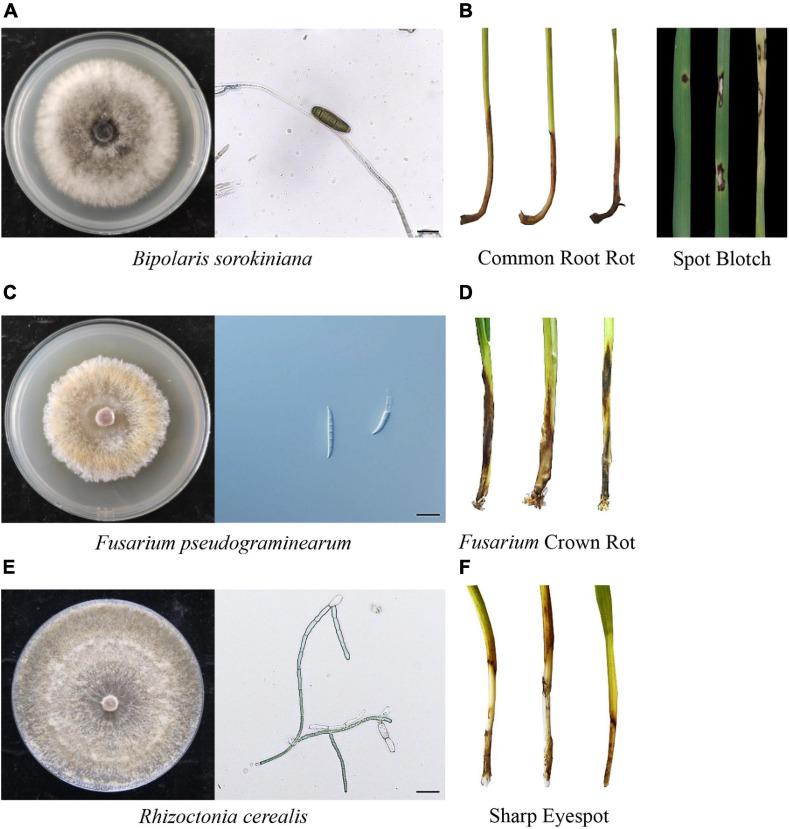
FIGURE 1.
Pathogenic profiles of Bipolaris sorokiniana, Fusarium pseudograminearum, and Rhizoctonia cerealis. (A) B. sorokiniana was cultivated on potato dextrose agar (PDA) medium and spores were directly collected. (B) Common root rot and spot blotch caused by B. sorokiniana. Infected wheat plants were easily pulled out, the stem base and root system felt wet, and black and brown striped spots can be observed in both the stem base and lower leaves. (C) F. pseudograminearum cultivated on PDA medium. Spores of F. pseudograminearum can be induced on carboxymethyl cellulose sodium (CMC) medium. (D) Fusarium crown rot caused by F. pseudograminearum. The stem base of infected wheat plants became dry and fragile, and was easily broken apart. Additionally, dark and red brown rot can be observed in the stem base. (E) R. cerealis was cultivated on PDA medium. (F) Sharp eyespot caused by R. cerealis. The typical lesions on wheat stem are elliptical or exhibit an “eye” shape with sharply dark brown borders. Scale bar = 20 μm.