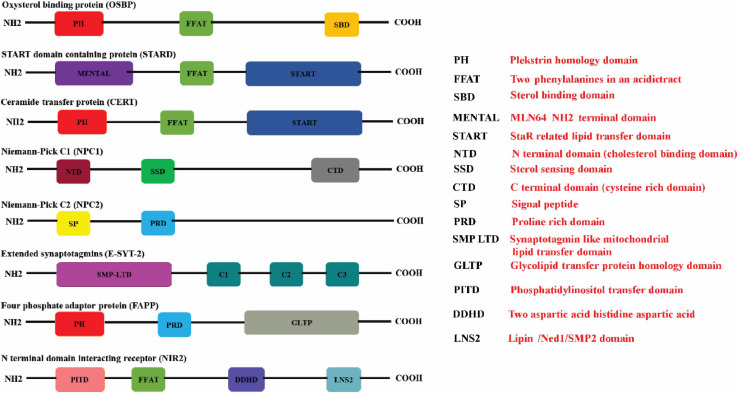
FIGURE 1.
Schematic illustration of the protein domains in the respective lipid transfer proteins. The (red boxes) represent the Pleckstrin homology domain (PH domain) which binds to phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate (PI4P) that is commonly present in OSBP, CERT, and FAPP. The FFAT motif which promotes interaction with ER-resident VAP proteins is represented in (green box) is present in OSBP, CERT, and STARD proteins. STEROL binding domain (dark yellow box), START domain (navy blue box), GLTP domain (gray box), and SMP domain (purple box) represents the characteristic lipid-binding domains specific for the individual LTPs. START proteins also have a multifunctional MENTAL domain (violet box) that binds to cholesterol. The E-Syts transfers glycerophospholipids through its mitochondrial-lipid-binding protein domain (SMP) (purple box). The E-Syts protein has a variable number of C2 domains (pine green boxes) which is responsible for Ca2+/phospholipid binding and protein–protein interactions. NPC1 has a cholesterol binding domain NTD (brown box), sterol sensing domain (SSD) (bottle green box) and a Cystine rich C terminal domain (dark gray box). Unlike NPC1, NPC2 consists of a signal peptide (butter yellow box) sensor and Proline rich domain (sapphire blue box). The proline rich domain is represented in (light blue box). The PITD of Nir2 is represented in (pink box) whereas LNS2 is represented as (teal colored box) (Created with BioRender.com).