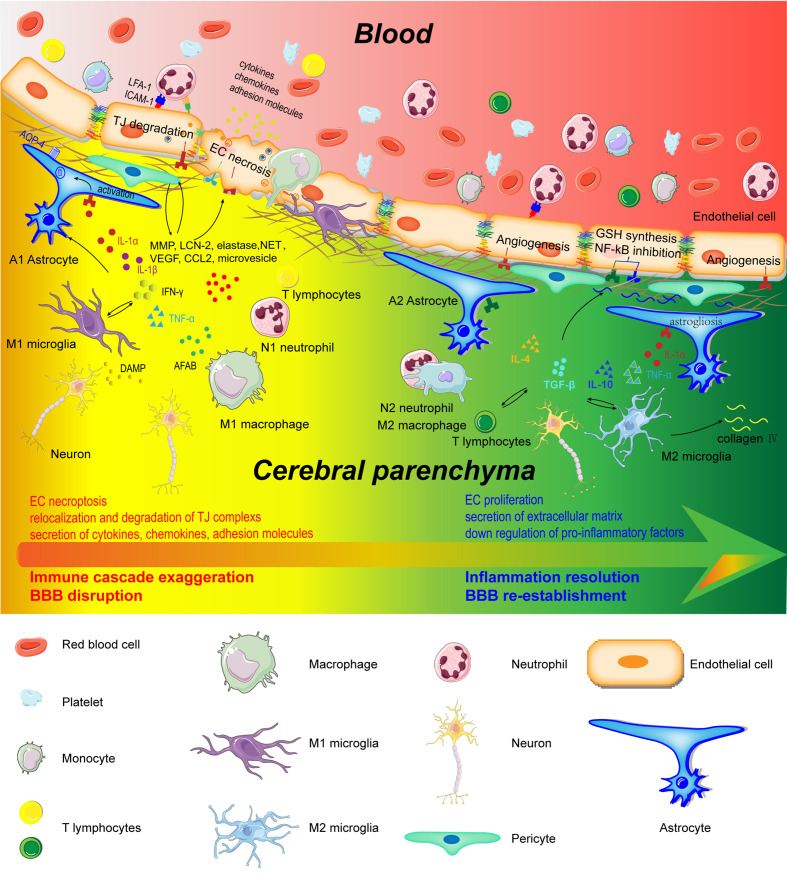
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of cerebral and peripheral immune cells regulating BBB integrity during early and later phases of ischemic stroke. Infiltrated neutrophils produce proteases (MMPs, proteinase 3, and elastase), lipocalin-2, NET, microvesicles, cytokines, and chemokines to destroy the BBB structure. M1-type monocytes secret cytokines and chemokines to degrade TJs. Perivascular microglia phagocyte ECs, which directly lead to endothelial dysfunction and BBB disintegration. In addition, M1 microglia disrupt BBB integrity through the production and secretion of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and CCL2), MMP9, and VEGF. A1 astrocytes directly exert deleterious effects on BBB through increasing VEGF, cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α), chemokines (CCL2 and CCL5), MMP, and LCN-2. However, in the recovery phase of AIS, these immune cells contribute to inflammation resolution and BBB re-establishment. N2 neutrophils promote engulfment of neutrophils by macrophages and inflammation resolution. Monocyte-derived M2 macrophages facilitate the expression of collagen IV and efferocytosis. Microglia directly protect BBB integrity through the secretion of IL-10 and TGF-β. A2 astrocytes are capable of secreting IL-2, IL-10, and TGF-β to accelerate inflammation resolution.