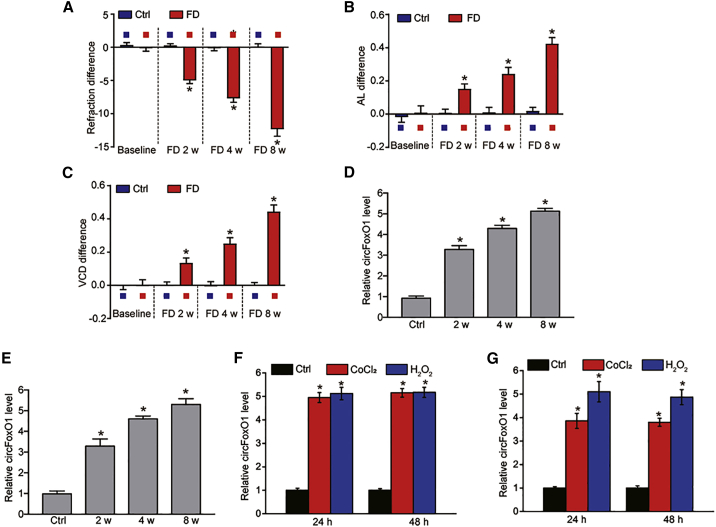
Figure 1.
Myopia leads to an increased level of circFoxO1 during choroidal vascular dysfunction
(A–C) The guinea pigs underwent monocular form deprivation (FD) using the translucent eye shield. Three ocular biometric parameters, including refractive state (A), axial length (AL; B), and vitreous chamber depth (VCD; C), were measured to verify the successful establishment of a myopia model (n = 6 retinas per group; Mann-Whitney U, Bonferroni test). (D) qRT-PCR assays were conducted to detect the expression of circFoxO1 in the choroidal samples of guinea pigs after 0 (control [Ctrl]), 2, 4, or 8 weeks of FD treatment (n = 6 retinas per group; Kruskal-Wallis test, Bonferroni test). (E) qRT-PCR assays were conducted to detect the expression of circFoxO1 in the choroid of C57BL/6 mice after 0 (Ctrl), 2, 4, or 8 weeks of FD treatment (n = 6 retinas per group; Kruskal-Wallis test, Bonferroni test). (F and G) circFoxO1 expression was detected by qRT-PCRs in RF/6A cells or primarily isolated choroidal endothelial cells (ECs) cultured in the medium containing normal medium (Ctrl), CoCl2 (200 μM), or H2O2 (100 μM) for 24 and 48 h (n = 4; ∗p < 0.05 versus Ctrl group, one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni test).