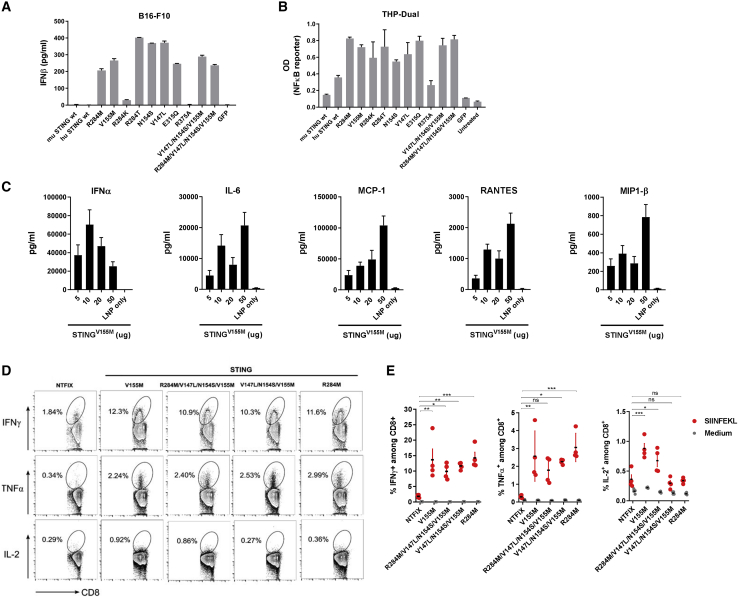
Figure 2.
Constitutively active STING variants encoded by mRNA demonstrated similarly potent IFN-inducing activity in vitro and vaccine adjuvant effect in vivo
(A) B16F10 cells were transfected with mRNA-encoded wild-type or constitutively active STING variants. The concentration of murine (m)IFN-β was determined by ELISA. (B) THP1-Dual NF-κB-inducible reporter cells were transfected as described in (A). At 24 h after transfection, NF-κB activation was evaluated by measuring the level of SEAP in supernatants. (C) C57BL/6 mice were injected intramuscularly with mRNA-LNP encoding STING at the indicated amounts. Serum cytokine levels were assessed at 6 h after injection. (D and E) C57BL/6 mice were immunized intramuscularly on day 0 and day 14 with mRNA-LNP (10 μg/mouse) coformulated into LNPs with OVA and caSTING variants. On day 21, the percentage of SIINFEKL-specific CD8+ T cells in spleens was determined by intracellular staining of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2 after a 4-h ex vivo stimulation with cognate peptide. Representative flow cytometry plots gated on total CD8+ T cells are shown. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments with four to five mice per group. Data plotted are mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.