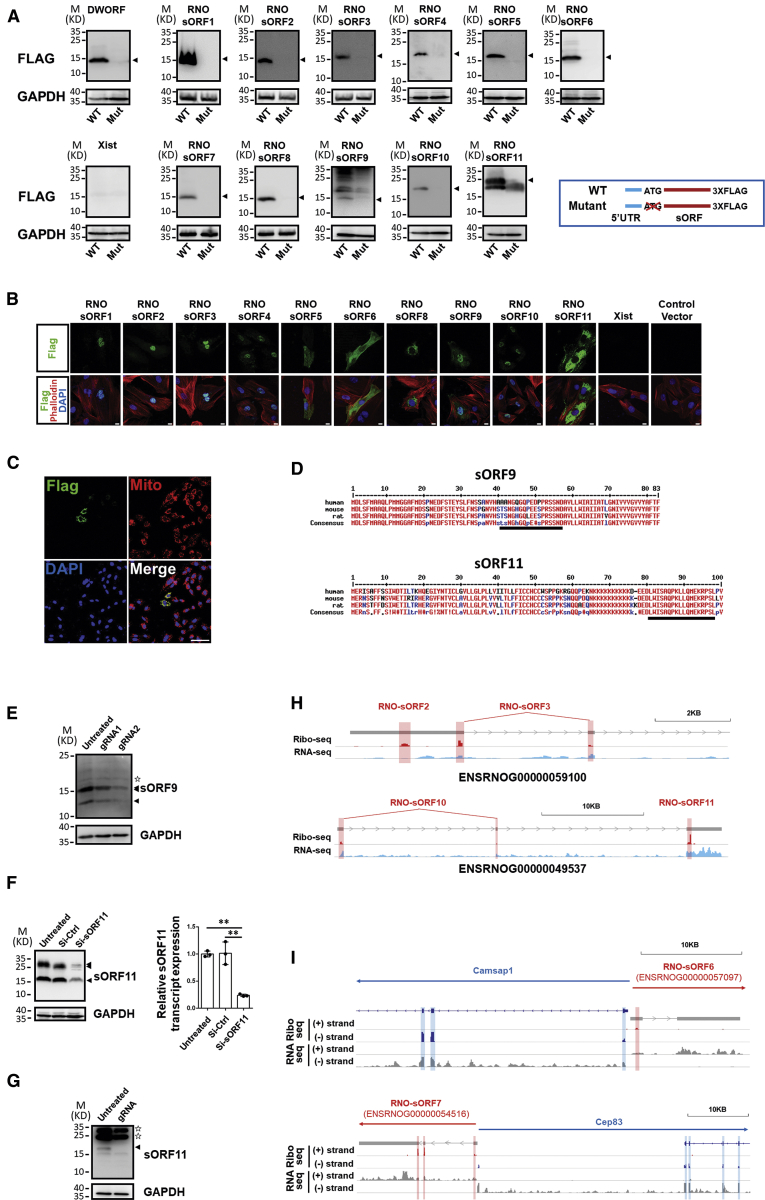
Figure 5.
Identification of short ORF (sORF)-coding micropeptide from hypertrophic cardiomyocytes
(A) Wild-type (WT) and mutant (Mut; ATG codon deletion) sORFs were cloned into a 3XFLAG-tagged expressing vector (inlet). Ectopic expression of flag-tagged micropeptides was detected by western blotting with anti-FLAG antibodies. The detected GAPDH expression serves as loading control. (B) The localization of micropeptides is determined by immunostaining for FLAG-tagged micropeptides in H9C2 cardiomyocytes transfected with micropeptide-overexpressing vectors. Cardiomyocytes were co-stained with phalloidin. Nuclei are indicated by DAPI. Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) The expression of FLAG-tagged RNO-sORF7 was detected in mitochondria in H9C2 cardiomyocytes transfected with overexpressing vector. Mitochondria are indicated with MitoTracker; nuclei are indicated by DAPI. Scale bar, 75 μm. (D) Amino acid sequence alignment of sORF9 and sORF11 from humans, mice, and rats. The peptide fragments used for antibody development are underlined. (E) Detection of sORF9 expression in untreated H9C2 cardiomyocytes and cells edited with the CRISPR-Cas9 system for frameshift mutation in sORF9. (F) Detection of sORF11 expression by western blotting and qRT-PCR in sORF11 knockdown H9C2 cardiomyocytes. n = 3 for each group. ∗∗p < 0.01. (G) Detection of sORF11 expression in untreated NIH 3T3 cells and cells edited with the CRISPR-Cas9 system for frameshift mutation in sORF11. The expression of GAPDH serves as the control. Arrowheads indicate specific bands, and stars indicate unspecific bands. (H and I) Examples for two micropeptides, which are coded by one transcript (H), and examples for micropeptides, which are coded by lncRNAs derived from the complementary DNA strand (I), in the IGV genome browser. Reads in Ribo-seq and RNA-seq are shown. sORF are shadowed in red, and annotated ORFs are shadowed in blue. Gene structures are shown by bars and lines with directions of transcription indicated (arrows).