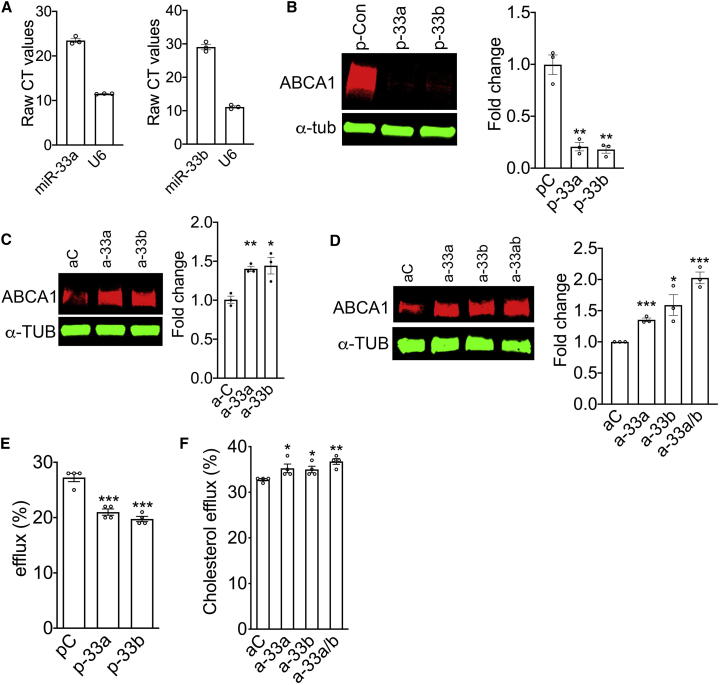
Figure 1.
miR-33 modulated ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux in RPE cells
(A) The expression of miR-33a and miR-33b was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR in primary human RPE cells (n = 3). (B) Western blot showing the expression of ABCA1 in primary human RPE cells 72 h after transfection with precursor miR control, miR-33a, or miR-33b (n = 3). (C) Western blotting demonstrating ABCA1 in primary human RPE cells 72 h post-transfection with control, anti-miR-33a, or anti-miR-33b (n = 3). (D) Western blotting demonstrating ABCA1 in ARPE-19 cells 72 h post-transfection with control, anti-miR-33a, anti-miR-33b, or anti-miR33a/b (n = 3). (E) TopFluor cholesterol efflux was measured in ARPE-19 cells transfected with precursor control miR, miR-33a, or miR-33b. (F) TopFluor cholesterol efflux was assessed in ARPE-19 cells ∼60 h after transfection with scrambled control, anti-miR-33a, anti-miR-33b, or-miR-33a/b ASO. pC, precursor scrambled control miR; aC, anti-miR control. All error bars represent ±SEM. (B–D) Expression levels were normalized to α-tubulin loading control, and statistical significance between groups was calculated by unpaired t test. (E and F) Each experiment was performed in quadruplicate and repeated ≥3 times, and statistical significance between groups was calculated by unpaired t test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.