Figure 7.
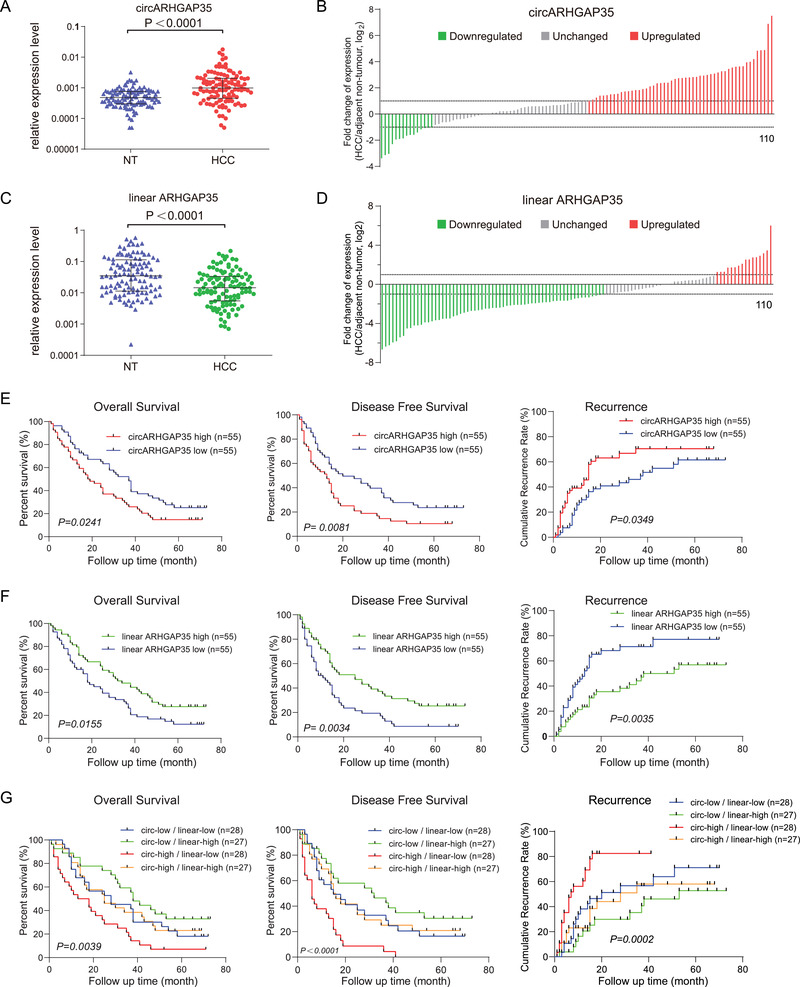
The upregulation of circARHGAP35 is associated with poor survival in cancer patients. A) The expression of circARHGAP35 in 110 paired HCC and adjacent non‐tumor (NT) liver tissues. Data were analyzed by paired Student's t‐test, n = 110. B) The fold change of circARHGAP35 expression in 110 paired HCC samples (downregulated, green; unchanged, gray; upregulated, red). C) The expression of linear ARHGAP35 in 110 paired HCC and adjacent non‐tumor (NT) liver tissues. Data were analyzed by paired Student's t‐test, n = 110. D) The fold change of linear ARHGAP35 expression in 110 paired HCC samples (downregulated, green; unchanged, gray; upregulated, red). E) Kaplan–Meier analysis of the correlation between circARHGAP35 expression and overall survival (OS), disease free survival (DFS), and recurrence in 110 HCC patients. F) Kaplan–Meier analysis of the correlation between linear ARHGAP35 RNA expression and OS, DFS, and recurrence in 110 HCC patients. G) The 110 HCC patients were divided into four groups according to the expression levels of circARHGAP35 and linear ARHGAP35 RNA. Kaplan–Meier analysis of the correlation between circARHGAP35/linear ARHGAP35 RNA expression and OS, DFS, and recurrence in 110 HCC patients. Log‐rank tests were used to determine the statistical significance for (E), (F), and (G).
