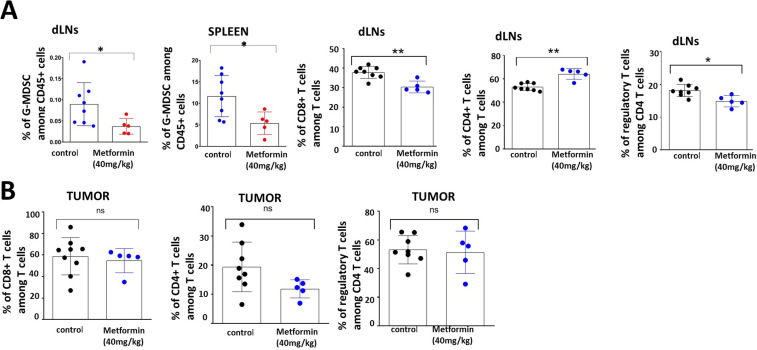
Figure 1.
Systemic and regional immune modulation by acute metformin exposure in tumor bearing mice. C57BL/6J male mice were inoculated subcutaneously with 1×106 mEER cells and the tumors were allowed to establish to an average size of 65 mm2 prior to treatment initiation. Beginning on day 18, metformin treated mice (n=5) received five consecutive daily doses of metformin (40 mg/kg) and control mice (n=8) received PBS delivered intraperitoneally. All mice were euthanized on day 23 post-tumor inoculation and tumor, spleen and draining lymph nodes (dLN) were harvested from the mice accordingly. Flow cytometry was used to characterize T-cell and myeloid cell subsets in spleen and inguinal lymph node (A) and tumor (B) tissues. Data are presented as means with error bars denoting SD. Experiment performed once. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ns, not significant; PBS, phosphate buffered-saline.