Figure 1.
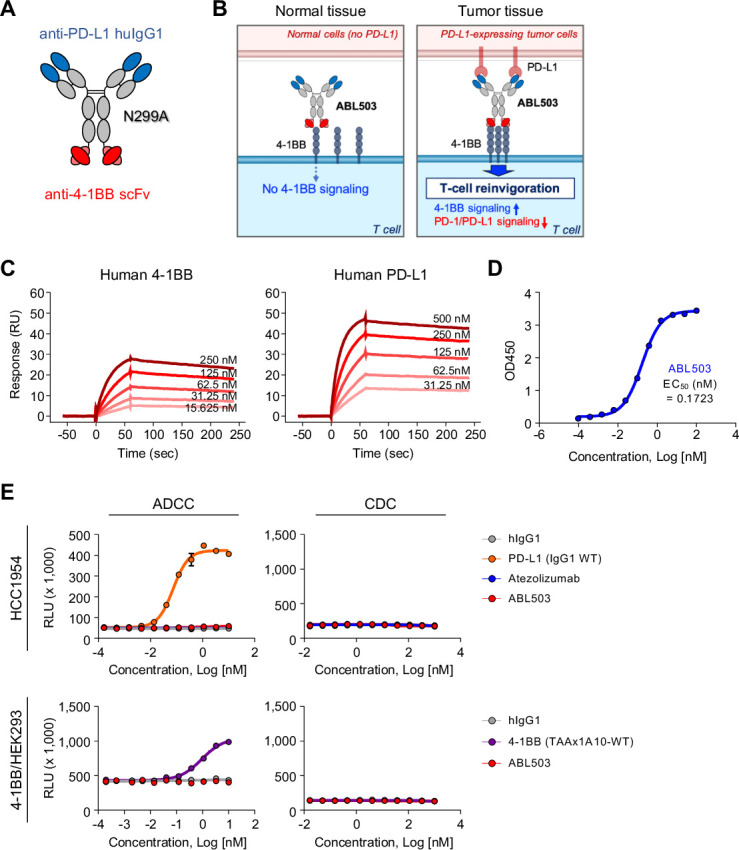
Novel tumor-targeting anti-PD-L1×4-1BB bispecific antibody (ABL503) simultaneously binds unique sites on its targets. (A) ABL503 was designed to target PD-L1 and 4-1BB at the F(ab)2 and Fc portions, respectively, which prevents the Fc portion from binding FcγR. (B) Schematic illustrating the mechanism of action of ABL503. (C) Surface plasmon resonance confirmed the binding of ABL503 to the targets 4-1BB (left) and PD-L1 (right) at the indicated concentrations. (D) Dual-antigen capture ELISA showed that ABL503 simultaneously bound 4-1BB and PD-L1 at the indicated antibody concentrations. The EC50 of ABL503 indicates the mean. (E) The capacity of inducing antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) was estimated by ADCC reporter bioassay during ABL503 treatment. The complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) efficacy of ABL503 was also measured by CDC assay. All experiments were performed by duplicated or triplicated samples.
