Fig. 6.
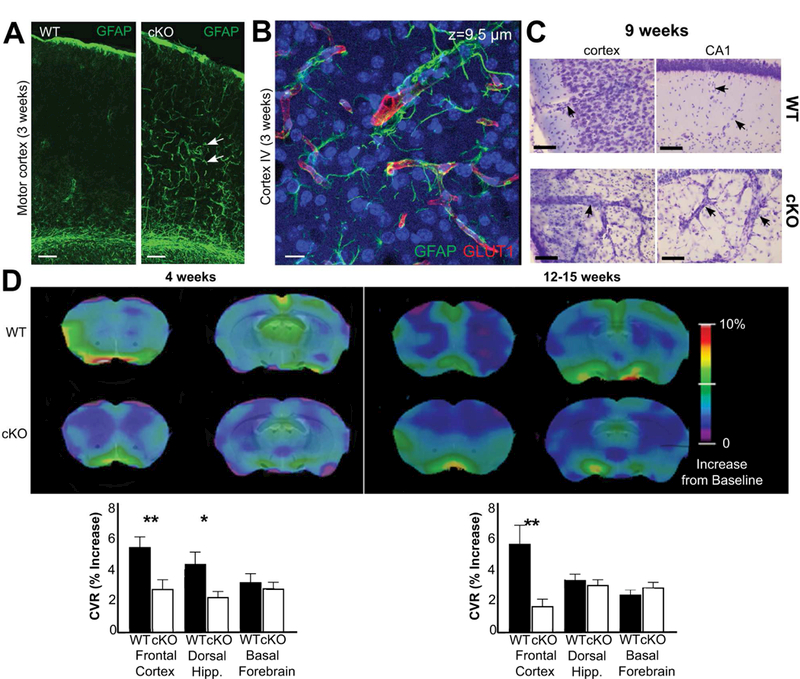
Glul knockout mice (cKO) had altered cerebral blood vessels with reduced ability to react to increases in CO2 levels. (A) There was increased GFAP labeling (green) in astroglial processes in 3 weeks old Glul cKO mice. The images from wildtype (WT) and cKO mice represent montages of three overlapping images acquired from the motor cortex. Scale bar 100 µm. (B) Z-stack image (total thickness 9.5 µm) acquired from motor cortex (layer VI) of the same cKO section as in A. Note increased GFAP labeling in astroglial processes surrounding blood vessels (red, GLUT1). Scale bar 100 µm. (C) Nissl staining shows changed vascular structures in the motor cortex and hippocampus CA1 of 9 weeks old cKO mice compared to WT littermates (processed in parallel). Scale bar 50 µm. (D) Impaired cerebrovascular reactivity in (as indicated) 4 and 12 – 15 weeks old cKO mice. Voxel-level maps of cerebrovascular reactivity (CVR), as defined by the relative increase of signal during CO2 challenge, averaged across each age/group. Maps are projected on two coronal slices of a structural mouse atlas. Region of interest-averaged CVR amplitudes are shown on bar graphs (bottom); cKO mice have impaired CVR response in the dorsal hippocampus at 12 weeks, and in the cortex at both time-points. Subcortical areas like the basal forebrain are unaffected in cKO animals. The most cranial slices (the left images on each sub-figure) are +1.2 mm from bregma, while the caudal slices (the right images on each sub-figure) are −0.6 mm from bregma. *p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01.
