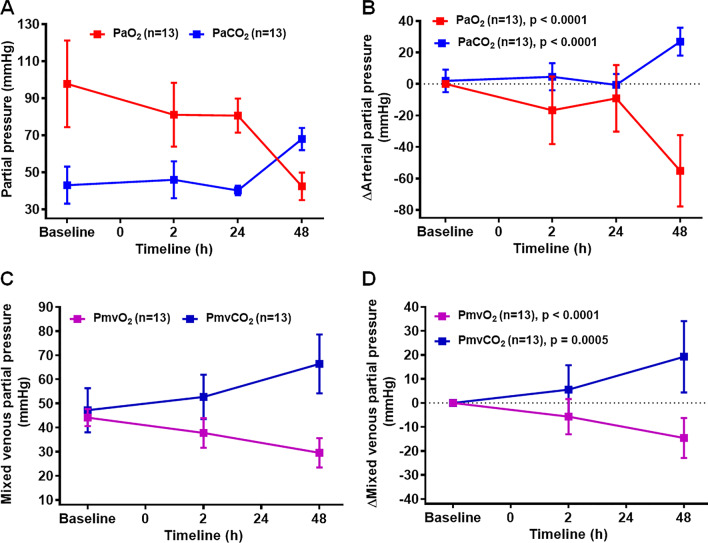
Fig. 5.
Smoke inhalation reduces PO2 with reciprocal increase in PCO2. Arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) and carbon-dioxide (PaCO2) levels were measured in SI group at baseline, 2 h, 24 h, and 48 h time points (A). Delta PaO2 (ΔPaO2) and delta PaCO2 (ΔPaCO2) values between baseline and different time points (B). Mixed venous partial pressure of pressure of oxygen (PmvO2) and carbon dioxide (PmvCO2) level were measured in SI group at baseline, 2 h, 24 h, and 48 h time points (C). Delta PmvO2 (ΔPmvO2) and delta PmvCO2 (ΔPmvCO2) values were calculated between baseline and different time points (D). Delta value for each parameter represented the difference with corresponding baseline values. PaO2 and PaCO2 levels were measured at 24 h for n = 8; PmvO2 and PmvCO2 levels were not measured at 24 h time line. Smoke inhalation started at 0 h time point. A p value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant