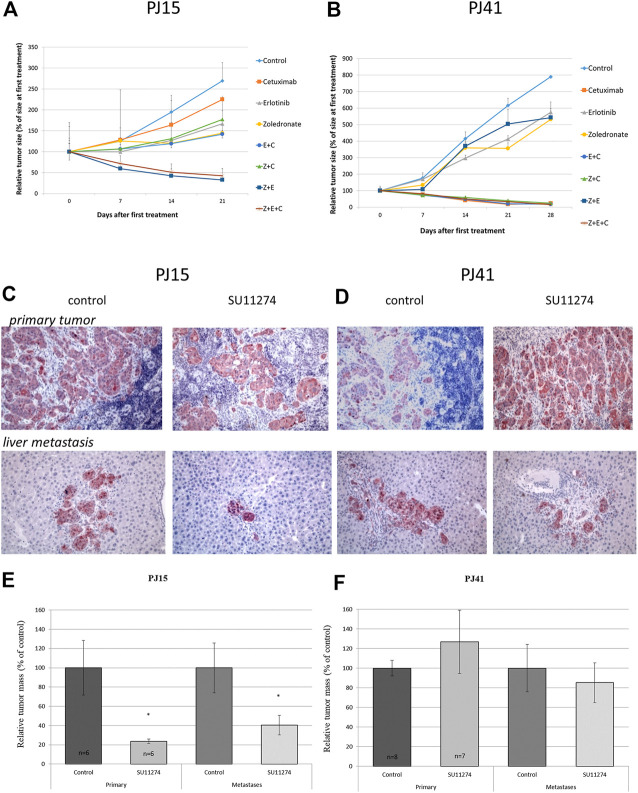
FIGURE 3.
In vivo effect of EGFR-, RAS- and c-MET-inhibitors on growth and metastatic colonization of HNSCC xenografts Subcutaneously growing HNSCC tumor xenografts ((A) PE/CA-PJ15, (B) PE/CA-PJ41) bearing mice were treated i.p. with the EGFR, Ras and c-MET inhibitors mono- and combination therapy as well. In the case of PJ15 cetuximab had no effect on tumor growth, but erlotinib and zoledronic acid decreased significantly the tumor volume either in monotherapy or in combination treatment. However, cetuximab had profound effect on tumor growth of PJ41 xenograft: all the investigated cetuximab-containing therapeutic regimes decreased dramatically the tumor volume. (C–D) Immunohistochemical detection of tumor cells using cytokeratin antibody in spleen (upper row) and liver (lower row) after colonization assay. In the case of cetuximab-resistant PJ15 (C) SU11274 treatment (right pictures in the panel) significantly decreased both the primary tumor mass and the number of tumor colonies in the liver compared to control (left pictures). The primary tumor mass was decreased to 20% of the control in treated animals, and the number of the liver colonies were decreased to less than 40% of the control group (E). However, SU11274 had no effect on either the primary tumor growth or liver colonization of cetuximab-sensitive PJ41 xenografts (F). Graph represent means ± SEM. Significance was measured by Mann-Whitney U-test. “C”: cetuximab; “E”: erlotinib, “Z”: zoledronic acid; “SU”: SU11274.