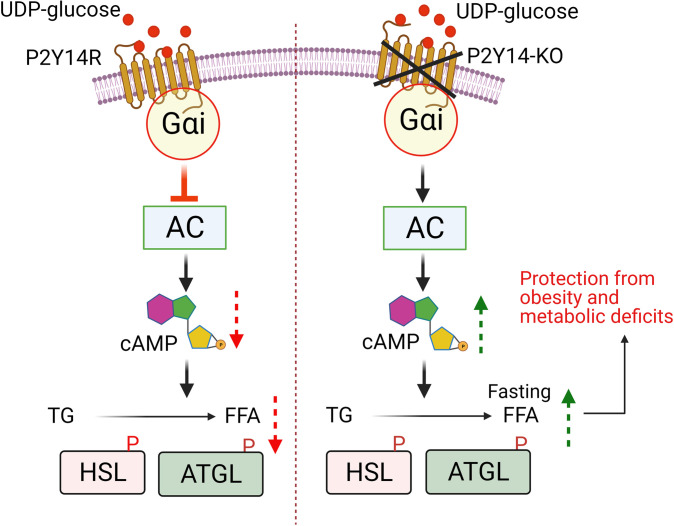
Figure 7. Molecular mechanism for the P2Y14R function in white adipocytes.
Activation of Gi-coupled P2Y14R in adipocytes inhibits lipolysis via decreasing cAMP levels resulting in decreased phosphorylation and activity of lipolytic enzymes. Adipocyte-specific KO of P2Y14R causes increase in cAMP levels, increasing phosphorylation and activity of lipolytic enzymes, enhancing lipolysis in fasting conditions. Mice lacking P2Y14R in adipocytes were protected from obesity and associated metabolic deficits on high fat diet. P2Y, purinergic; AC, adenylate cyclase; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; HSL, hormone-sensitive lipase; ATGL, adipose triglyceride lipase; TG, triglycerides; FFA, free fatty acid; P, phosphorylation.