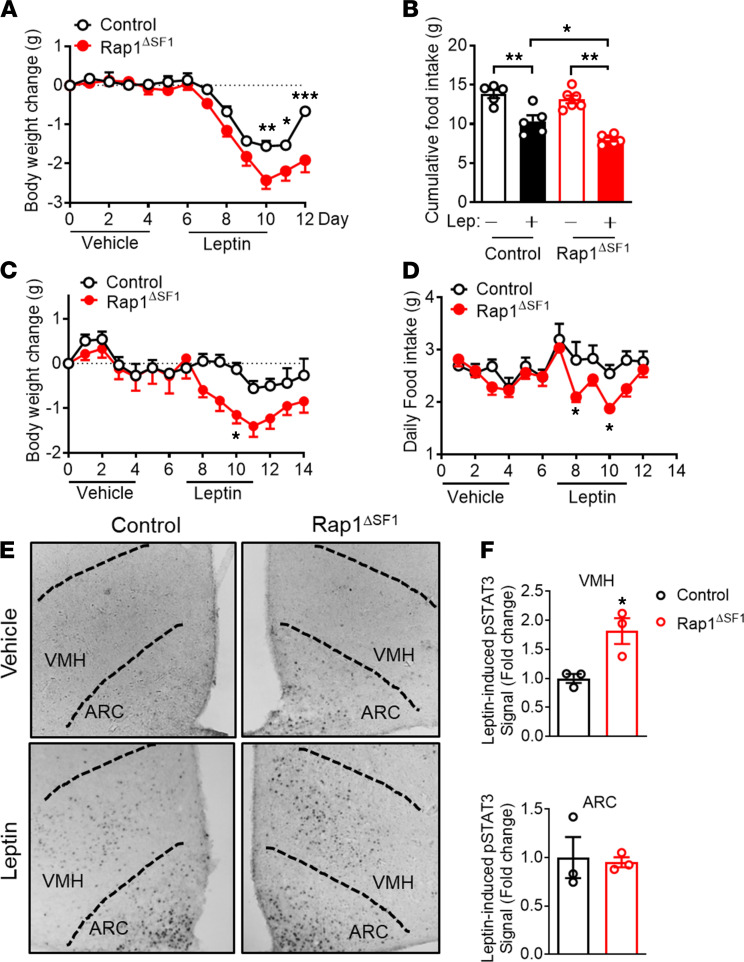
Figure 6. Leptin responsiveness is increased in Rap1ΔSF1 mice.
(A and B) Leptin (3 mg/kg, twice a day, i.p.) or vehicle was administered to normal chow–fed lean Rap1ΔSF1 or control mice (n = 5–6). Shown are the body weight (A) and cumulative food intake (B). (C and D) HFD-fed Rap1ΔSF1 or control mice (15 weeks of HFD) were injected with leptin (3 mg/kg, twice per day, i.p.) or vehicle (n = 6–7). Body weight (C) and food intake (D) were measured every day. (E and F) Leptin (3 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered to the indicated mice (n = 3 per group). (E) Representative immunohistochemistry images for phosphorylated STAT3, original magnification, ×100. (F) Quantification of immunohistochemistry. Age- and body weight–matched cohorts were used (A–F). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 for 2-tailed t tests (F), 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (B) or 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (A, C, and D). All error bars are mean ± SEM.