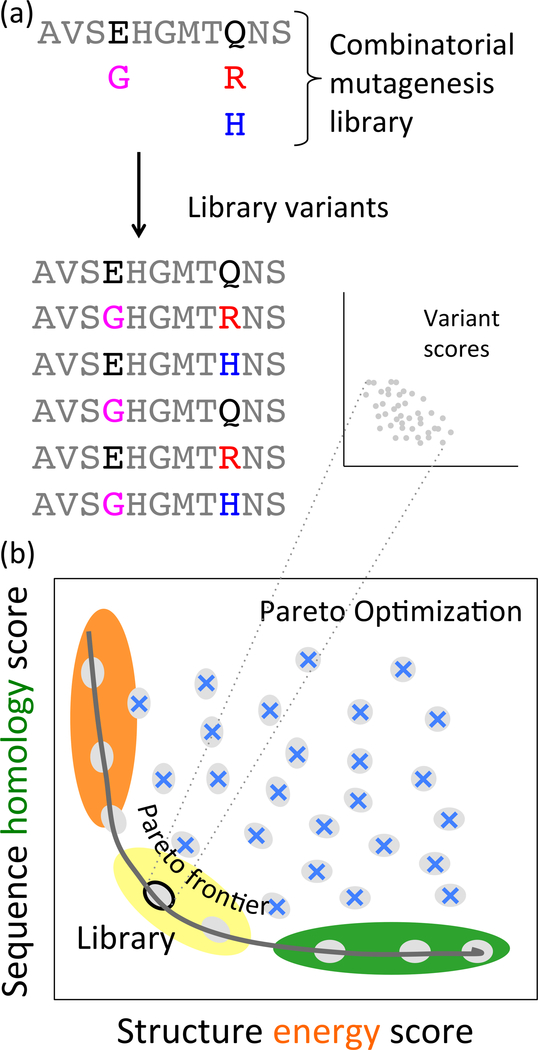
Fig. 1:
Combinatorial mutagenesis libraries, (a) A tiny example combinatorial mutagenesis library, with two possible amino acids at one position and three possible amino acids at another position, yielding six variants representing all combinations of these choices, (b) POCoM optimizes libraries to balance two objectives, here sequence homology and structure energy, each to be minimized. It evaluates a library in terms of the average score of its variants. Pareto optimal designs, comprising the Pareto frontier (on the black curve), make the best trade-offs between the two objectives, while dominated designs (blue Xes) are worse on both.