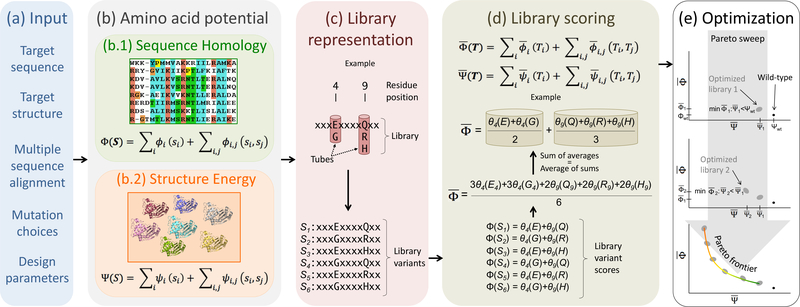
Fig. 2:
POCoM overview, (a) Input data are collected and preprocessed, (b) Amino acid potentials are extracted from the target’s sequence and structure, (c) Possible sets of amino acids are determined at each position, thereby defining choices representing a library, (d) Scores for each position-specific amino acid set, or “tube”, are averaged in order to assign contributions to the sequence homology and structure energy library scores, (e) Pareto optimal libraries are optimized with a sweeping technique that repeatedly finds the next undominated design as that with the best while constrained to have reduced .