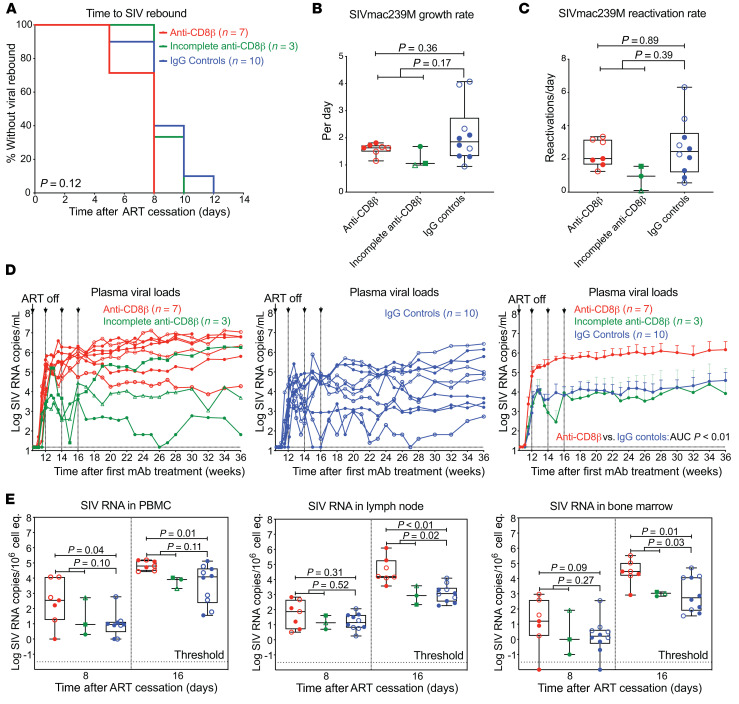
Figure 8. Effect of CD8+ T cell depletion on SIV infection dynamics after ART withdrawal.
(A) Kaplan-Meier analysis of SIV rebound kinetics in RMs with effective CD8+ T cell depletion (red; n = 7) and RMs with incomplete CD8+ T cell depletion (green; n = 3) versus IgG isotype controls (blue; n = 10). (B and C) Quantification of overall viral growth rates and SIVmac239M clonal reactivation rates in plasma by high-throughput sequencing after ART cessation. (D) Individual pvl profiles of RMs in each treatment group. Left panel shows anti-CD8β–treated RMs with effective CD8+ T cell depletion versus RMs with incomplete CD8+ T cell depletion (green), while the middle panel shows IgG isotype controls (blue). Right panel shows mean (+SEM) pvl profiles of RMs stratified by treatment group (limit of detection, 15 RNA copies/mL). Wilcoxon’s rank-sum test was used to determine significance of differences in the AUC of pvl between 14 and 20 weeks after mAb treatment (unadjusted P values shown). (E) Quantification of cell-associated SIV RNA in PBMCs, LNs, and BM (copies per 1 × 106 cell equivalents) at 8 and 16 days after ART cessation. Plots show jittered points with a box from first to third quartiles (IQR) and a line as the median, with whiskers extending to the farthest data point within 1.5 × IQR above and below the box, respectively. In B, C, and E, Wilcoxon’s rank-sum test was used to determine the significance of differences between treatment groups, first excluding RMs with incomplete CD8+ Tm depletion, and then including all treated RMs versus IgG controls (unadjusted P values shown). Closed symbols indicate Mamu-A*01+ RMs and open symbols indicate Mamu-B*08+ RMs.