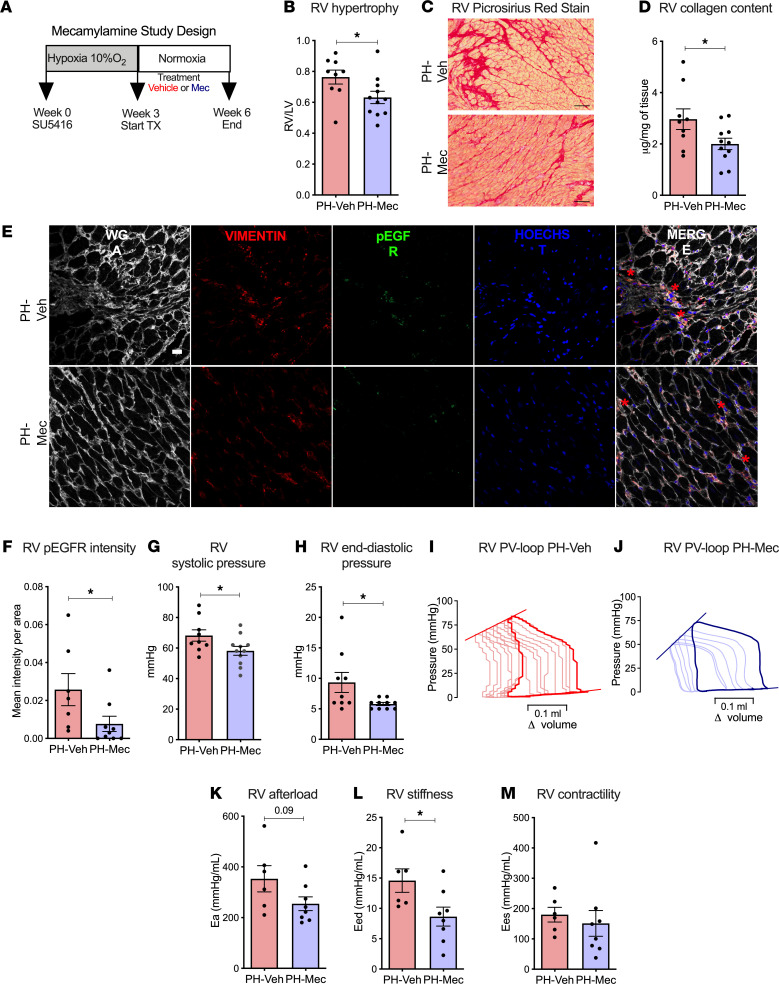
Figure 7. Treatment with nAChR blocker mecamylamine improves RV function in experimental pulmonary hypertension.
(A) Study design for mecamylamine (Mec) treatment. PH rats were randomized into vehicle (PH-Veh) or Mec (20 mg/kg, i.p., PH-Mec) treatment daily for 3 wks (n = 9 PH-Veh/11 PH-Mec). (B) RV weight normalized to the respective LV weight (n = 9 PH-Veh/11 PH-Mec). (C) Representative images of the RV from vehicle- and Mec-treated animal stained with Picrosirius red. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) Collagen content in RV homogenates from vehicle- and Mec-treated PH rats (n = 7 PH-Veh/9 PH-Mec). (E) Representative immunofluorescence staining for pEGFR (Y1068) in the RV from vehicle- and Mec-treated rats. Wheat germ agglutinin to outline the cardiomyocytes in white (Alexa 647), vimentin for cardiac fibroblasts in red (Alexa 594), pEGFR in green (Alexa488), and Hoechst for nuclei in blue. Red asterisks show colocalization of pEGFR with fibroblasts. Scale bar: 20 μm. (F) Quantification of area of pEGFR immunofluorescence in the RV (n = 7 PH-Veh/9 PH-Mec). (G and H) Invasively measured RV systolic pressures (n = 9 PH-Veh/11 PH-Mec) (G) and RV end diastolic pressures (n = 9 PH-Veh/10 PH-Mec) (H). (I and J) Representative examples of pressure-volume relationship for vehicle- (I) and Mec-treated (J) PH rats. (K–M) Arterial Elastance (Ea) as a measure of RV afterload (n = 6 PH-Veh/8 PH-Mec) (K), end-diastolic pressure-volume relationship (Eed) as an indicator of RV stiffness (n = 6 PH-Veh/8 PH-Mec) (L), and end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (Ees) as a measure of RV contractility (n = 6 PH-Veh/8 PH-Mec) (M) derived from the PV loop analyses. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Two-tailed unpaired t tests or Mann-Whitney U test between vehicle and Mec treatment. *P < 0.05. Ea, arterial elastance; Eed, end-diastolic pressure-volume relationship; Ees, end-systolic pressure-volume relationship; LV, left ventricle; Mec, mecamylamine; PH, pulmonary hypertension; RV, right ventricle; RVSP, RV systolic pressure; RVEDP, RV end diastolic pressure; or RV contractility; WGA, wheat germ agglutinin.