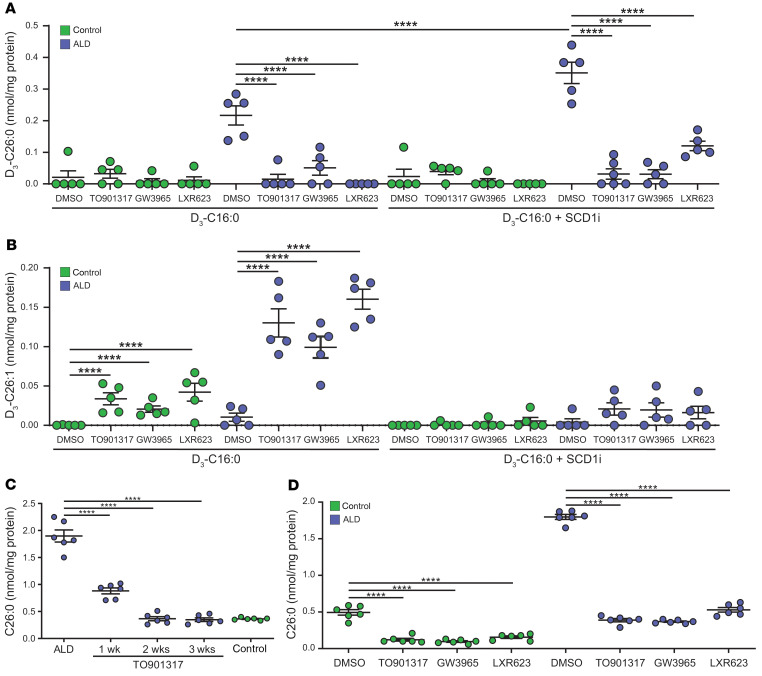
Figure 5. LXR agonists lower saturated VLCFA levels under acute and chronic exposure by shifting synthesis toward monounsaturated VLCFAs.
(A and B) LXR agonists reduce de novo saturated VLCFA synthesis (A) and reroute toward monounsaturated VLCFA synthesis (B). Control (n = 5) and ALD (n = 5) fibroblasts were cultured for 3 days with 100 μM D3-C16:0 without and with SCD1i combined with 5 μM TO901317, 1.5 μM GW3965, or 1.5 μM LXR623. De novo saturated VLCFA synthesis was assessed by measuring the levels of D3-C26:0 synthesized from D3-C16:0 (A). De novo monounsaturated VLCFA synthesis was assessed by measuring the levels of D3-C26:1 synthesized from D3-C16:0 (B). Inhibition of SCD1 enzymatic activity (SCDi) results in enhanced D3-C26:0 synthesis and a complete block in D3-C26:1 synthesis in ALD fibroblasts. (C) Chronic exposure to TO901317 normalizes endogenous C26:0 levels in ALD fibroblasts. ALD (n = 6) fibroblasts were cultured without and with 5 μM TO901317 up to 3 weeks. Total accumulated C26:0 levels were analyzed and compared with untreated control fibroblasts (n = 5). (D) Chronic exposure to LXR agonists normalizes endogenous C26:0 levels in control and ALD fibroblasts. Control (n = 5) and ALD (n = 5) fibroblasts were cultured for 3 weeks without and with 5 μM TO901317, 1.5 μM GW3965, or 1.5 μM LXR623, and the C26:0 levels were analyzed. Final concentration DMSO in culture medium was less than 1% (vol/vol). Data are represented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance determined with 1-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. ****P < 0.0001.