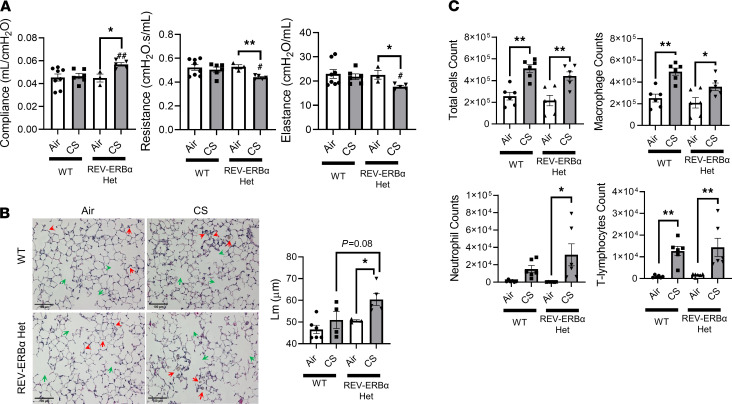
Figure 7. Altered airspace enlargement, lung mechanics, and inflammation were induced by chronic CS exposure in REV-ERBα Het mice.
Lung mechanics, inflammatory cell influx in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and airspace enlargement induced by chronic CS exposure (4 months) were determined by Flexivent, flow cytometry, and lung morphometry. (A) Lung mechanics (lung compliance resistance and elastance) were measured after chronic CS exposure. (B) Lung histological analysis were conducted using H&E-stained sections, and mean linear intercept (Lm) analysis was performed using Metamorph software (original magnification, ×20; scale bar: 100 μm) from H&E-stained images (green arrows indicated airspace enlargement and red arrows indicated inflammatory responses). (C) Total cell was counted by Bio-Rad cell counter using Trypan blue staining. Differential inflammatory cell counts (macrophage, neutrophil, and T lymphocytes) were determined (cells/mL) by flow cytometry. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 5–10; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, between groups; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 compared with CS-exposed WT group; 1-way ANOVA with Šidák correction).