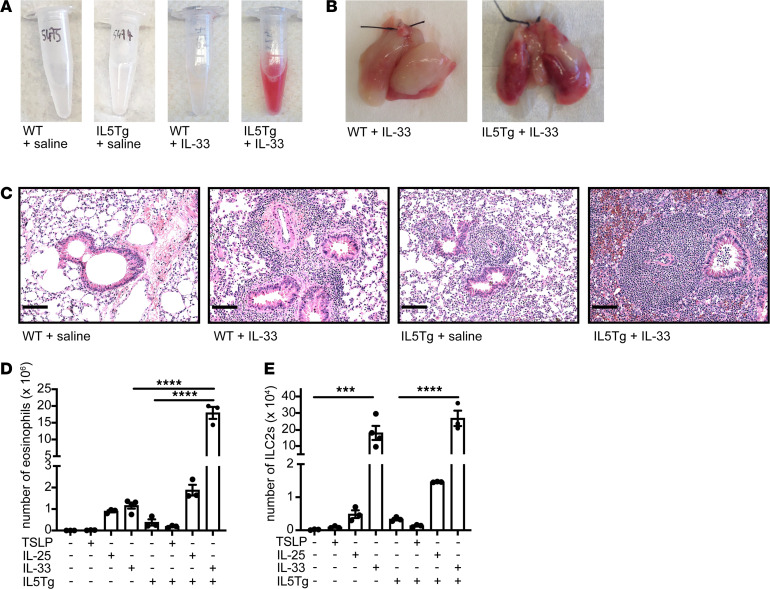
Figure 2. IL-33 and hypereosinophilia synergize to cause eosinophilic vasculitis in mice.
(A) Representative bronchoalveolar lavage and (B) representative whole lungs from IL-33–treated WT or IL5Tg mice. Images in A and B are representative of 3 or more mice/group, in a minimum of 3 independent experiments. (C) H&E staining of lungs from representative IL-33–treated WT or IL5Tg mice, as shown in A and B (original magnification, ×20). Scale bars: 100 μm. (D) Eosinophils or (E) ILC2s in BAL. Data are presented as ± SEM. ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001 by 1-way ANOVA with Sidak post hoc testing. n = 3–4 mice/group. BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; ILC2s, type 2 innate lymphoid cells.